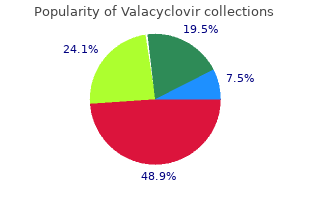
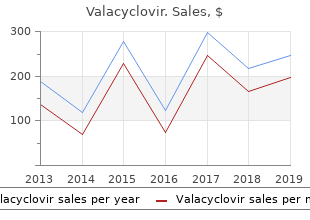
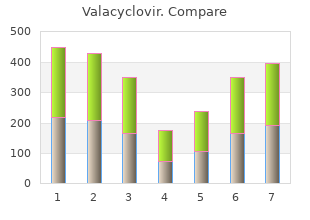
Valacyclovir
University of North Texas. E. Spike, MD: "Order Valacyclovir online in USA - Effective Valacyclovir no RX".
Appendix Page 8 Molars Maxillary Mandibular Second (#2) First (#3) Second (#31) First (#30) c c g g f Buccal f j j c c Lingual i b b b b Mesial j j i a a Occlusal 1 2 1 2 5 3 4 3 4 d d d d d d h Lingual Lingual h Lingual Lingual k k k k Refer to letters a–k on back buy valacyclovir american express hiv infection rates alberta, which describe these features 1000mg valacyclovir sale hiv infection rates africa. First molar roots are more divergent and widely sep- arated compared to second molars roots order genuine valacyclovir on line antiviral para que sirve, which are a. Mandibular crowns are wider mesiodistally than more parallel and closer together (facial and lingual faciolingually, resulting in a more rectangular or views). There is more taper (narrowing) from the distal the faciolingual dimension slightly greater than the proximal contact to the cervical line on first molars mesiodistal dimension and are more square or rhom- than on second molars due to the presence of the boid in outline (k) (occlusal views). Mandibular molars usually have two roots (a longer mesial and a shorter distal root) versus maxillary h. There is more taper (narrowing) from the buccal to molars, which have three roots (the longest lingual, lingual on second molars due to their smaller dis- the shorter mesiobuccal, and the shortest distobuc- tolingual cusp compared to less taper on maxillary cal root) (facial or lingual views). First molars are more likely to have a fifth cusp, the distobuccal cusp, compared to mandibular molars, cusp of Carabelli (located on the mesiolingual cusp) which primarily have two transverse ridges that run compared to second molars, which do not normally directly buccolingually (occlusal views). Mandibular second molars have four cusps (with more acute or sharper mesiobuccal and dis- (mesiobuccal = 1, distobuccal = 2, mesiolingual = 3, tolingual angles and more obtuse or less sharp dis- and distolingual = 4) with a “cross” pattern of occlusal tobuccal and mesiolingual angles) is more twisted grooves compared to first molars, which most often on second molars than on first molars (that is, have five cusps (the same four cusps as on the acute angles are more acute and obtuse angles are second molar, plus a smaller distal cusp = 5) with more obtuse on maxillary second molars) (occlusal a more zigzag central groove pattern (facial or views). Primary anterior tooth crowns have bulges in the root length compared to permanent teeth (facial cervical third of the labial and lingual surfaces. Primary maxillary canines are about as wide mesi- that occupies up to one third of the cervicoincisal odistally as they are long incisogingivally. Mandibular crown length, and the labial bulge is seen as a promi- canines are longer incisocervically and narrower nent convex cervical ridge (proximal views). Primary mandibular canines have their distal cusp narrower (thinner) mesiodistally than on permanent ridges longer than their mesial cusp ridges (as do all anterior teeth (facial view). Roots of maxillary and mandibular primary anterior nent maxillary first premolars) (facial views). There are often four cusps: two larger cusps (like a primary second molars compared to permanent or maxillary premolar), the mesiobuccal cusp (1) wid- secondary molars, where the first molars are larger est and longest and the mesiolingual cusp (2) the (compare all views, not labeled as “b”). Primary molar crowns have a narrow chewing sur- distobuccal (3) and the inconspicuous, sometimes face, or occlusal table, buccolingually compared to absent, distolingual (4) (occlusal views; see corre- the entire tooth width buccolingually (proximal sponding numbered cusps). Buccal cusps are not sharp; cusp ridges meet at a cal cusp from the indistinct distobuccal cusp (buccal wide (obtuse) angle (buccal views). The crown is wider faciolingually than mesiodistally mesially (proximal views), so the facial cervical lines like a maxillary premolar (occlusal views). There are three fossae: a large mesial triangular no root trunk compared to secondary molars (buccal fossa, a medium central fossa, and a minute distal views). The mesial marginal ridge is overdeveloped, almost resembling a cusp (buccal and occlusal views). The occlusal table is wider mesiodistally than bucco- pressed toward the distal (occlusal views). The mesial surface converges to the lingual with secondary teeth, where the mesiolingual cusp is an acute and prominent mesiobuccal angle of the larger than the mesiobuccal cusp (occlusal views). The occlusal table is larger distal to the transverse sus permanent first molars, where the distal cusp is ridge with a larger distal fossa and a smaller mesial usually considerably smaller (occlusal views). Sixth edition Copyright © 2018 by Wolters Kluwer © 2012, 2007, 2002, 1987, 1981 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins All rights reserved.
The muscles abduct the second and fourth fingers and move the middle finger either medially or laterally buy valacyclovir without prescription hiv infection during menstruation. The thumb can be opposed with any of the four other digits depending on the shape of the object to be held and the type of manipulation required buy valacyclovir with visa antiviral elderberry extract. However valacyclovir 1000 mg discount hiv infection unprotected penetration, there are subtler or less easily delineated patterns of symptoms in the hand, particularly when pain is diffuse or poorly localized. Are there neurologic qualities to the pain or characteristics typical of a common nerve lesion? Ask about occupation and other activities that are associated with neck problems, the relationship with sleep posture, and frequent headaches. However, pain in this condition is often poorly localized at initial presentation. Tingling/pins and needles/numbness Make sure both you and the patient understand what you each mean by these terms: • Symptoms usually denote cervical nerve root or peripheral nerve compression, although they can reflect underlying ischaemia. Pain arising from bone Pain in the hands arising from bones may be difficult to discriminate. Radiographs will often lead to confirmation of the diagnosis: • The most common tumour in the hand is an enchondroma. A history suggestive of ischaemic pain in the hands is rare in rheumatologic practice. Persistent ischaemic digital pain can complicate systemic sclerosis and severe Raynaud’s (see Chapter 13): • Digital vasomotor instability (e. Patients with carpal tunnel syndrome, for example, can complain of the hand swelling at night. This most commonly affects the middle and ring fingers, and is prevalent among professional drivers, cyclists, and those in occupations requiring repeated use of hand-held heavy machinery. Examination of the hand: adults The following sequence is comprehensive, but should be considered if a general condition is suspected. Inspection of the nails and fingers • Pits/ridges and dactylitis are associated with psoriatic arthritis (see Plate 8 and Chapter 8). The skin may be initially puffy, but later shiny and tight and, with progression, atrophic with contractures. Note any deformity of digits • Deformities tend to occur with long-standing polyarticular joint disease, e. Inspect the palm and dorsum of the hand • Palmar erythema is not specific, but is associated with autoimmune disorders of connective tissue and joints. Palpation of joints and nodules Palpation of joints and nodules is best done using thumb pads with the patient’s wrist supported: • Swelling should be noted for site, consistency, tenderness, and mobility. Osteophytes and exostosis are periarticular or at sites of pressure, may be tender, but are always fixed (see Plate 7d). Palpate tendons in the palm or on the volar aspect of the phalanges • Thickening, tenderness, and crepitus suggest tenosynovitis, but tenosynovitis can be hard to spot if it is mild. Discriminate Dupuytren’s disease from flexor tendinopathy Dupuytren’s disease (a fascia contracture) typically involves the fourth and fifth fingers (40% bilateral). It is associated with epilepsy, diabetes, and alcoholism, and usually is not painful. Tc- labelled human immunoglobulin is more specific for detecting patterns of synovitis in children and adults.

Effectiveness only against enveloped viruses Concept: Pathogen inactivation methods are currently for use on certain platelet and plasma products 1000 mg valacyclovir sale hiv infection undetectable viral load, and knowledge of the mechanism by which different pathogens are inactivated is important for understanding the benefts and limitations offered by these methods purchase valacyclovir 500 mg amex xl3 accion antiviral. The synthesis of cytokines is completely inhibited by the Intercept system during platelet storage buy generic valacyclovir 1000mg online anti viral ear drops, a fact that may translate into reducing the number of febrile nonhemolytic transfusion reactions (Answer D). Pathogen inactivation for blood products does not involve a possible mechanism by which peptidoglycans that are forming the bacterial wall are denatured (Answer A). Pathogen inactivation is effective against a broad variety of microorganisms, including enveloped and nonenveloped viruses, Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, spirochetes, and protozoa (Answer E). In short, S-303 is a modular compound that enables nucleic acid targeting and crosslinking, thereby preventing nucleic acid replication. The nonreactive byproduct formed after reaction of the S-303 compound with nucleic acids or by decomposition is S-300. The other choices (Answers A, B, D, and E) are incorrect based on the earlier discussion. During a local mobile high-school blood drive, a 17-year-old female who is a frst-time donor and eligible for donation of whole blood felt light-headed, weak, and nauseous during the donation. Her blood pressure dropped from 120/80 to 90/65 mmHg, and pulse decreased from 75 to 60. Although the majority of reactions are mild, moderate to severe reactions that lead to loss of consciousness, seizure-like activity, and severe injury do occur. The most common systemic donor reaction is presyncope or a vasovagal reaction characterized by dizziness, nausea, vomiting, pallor, weakness, sweating, and hyperventilation. Risk factors include young age, frst time donation, low weight, and an inattentive phlebotomist. Interventions include cold compresses around the neck and shoulder area, recumbent position, loosening of tight clothes, and reassurance from collection staff. Vasovagal reactions should be differentiated from hypotension due to arterial puncture and rapid blood loss. Arterial puncture occurs when the needle penetrates through the vein and enters the underlying artery. In addition, severe pain and rapid (pulsatile) flling of the bag with bright red blood occur during an arterial puncture. Treatment consists of discontinuing the donation and applying pressure to the site for a long period of time. Answer: C—The signs and symptoms described in the clinical vignette are consistent with a vasovagal reaction. This is a whole blood donation and thus, the donor is not exposed to citrate (Answer A). The symptoms are not consistent with allergic reaction or seizure (Answers B and E). Due to donor’s signs and symptoms, the whole-blood collection was stopped and only 375 mL of whole blood was collected in a 450 mL collection bag. What is the most appropriate next step for the hospital blood bank and/or the blood establishment to take? Labeling events include those that occur during the labeling process, which you didn’t discover until after you have distributed the product.
These procedures merely to remove the aneurysm but to restore circulation to all vital tributaries discount 500mg valacyclovir fast delivery hiv aids infection timeline. Further improvements in surgical adjuncts and in hybrid surgical/endovascular techniques will make this goal achievable in an ever larger propor- tion of patients than is possible today purchase 1000mg valacyclovir with mastercard hiv infection symptoms signs. On the treatment of aneurism by elec- aortic aneurysm with restoration of vascular continuity using a fabric graft generic valacyclovir 1000mg fast delivery antivirus website. Greenwich Medical Media, London, Successful resection of fusiform aneurysm of aortic arch 2001: 73−78. Intervention chirurgicale directe pour un aneu- Henry Ford Hospital International Symposium on Cardiac rysme de la crosse de l’aorte, ligature du sac. Med from vinyon N cloth in bridging arterial defects: experimen- News 1888; 53: 462−466. Surgical considerations of intra- of preparing woven Dacron aortic grafts to prevent intersti- thoracic aneurysms of the aorta and great vessels. Definitive treatment of saccular aneurysms of mosis: improved results in the treatment of aneurysms of the the aorta with excision of sac and aortic suture. The surgical vision closure of ventricular septal defects in eight patients treatment and the physiopathology of coarctation of the by means of controlled cross circulation. Application of a mechanical heart and lung studies regarding its surgical correction. Thoracic and clinical appraisal of coarctation four to seven years after Cardiovascular Surgery, 4th edn. Preliminary obser- aorta and aortic arch using circulatory arrest and retro- vation on the use of human arterial grafts in the treatment grade perfusion] Nippon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi 1988; of certain cardiovascular defects. Ann Thorac shunts to permit occlusion, resection, and frozen homologus Surg 1986; 42: 273−281. Total excision of trophrenic respirations, an artificial pacemaker for cardiac the aortic arch for aneurysm. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1955; 101: standstill and radio-frequency rewarming in general hypo- 667−672. Ann Thorac Surg 2005; aid of hypothermia: experimental accomplishments and the 80: 2166−2172. Ann Thorac Surg 2002; 74: plications after cardiopulmonary bypass: cerebral protection 1803S−1805. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1992; 103: hypothermia and circulatory arrest in the surgical treat- 617−621. Resection of the aortic arch Intentional left subclavian artery occlusion by thoracic aortic using deep hypothermia and temporary circulatory arrest. Combined approach in acute aortic dissection: preliminary clinical results with to stent-graft treatment of an aortic arch aneurysm. Extensive aortic replace- for distal aortic arch aneurysm: combined cervical branch ment using “elephant trunk” prosthesis. Elephant trunk technique in complex aortic pathology: the “bidirectional” procedure: newer indications and uses. Surgical Treatment of elephant trunk technique used for treatment of complex Aortic Aneurysms.