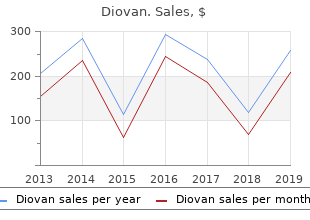
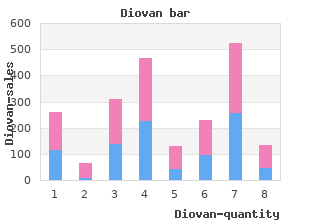
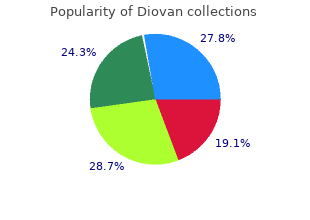
Diovan
University of South Dakota. K. Dudley, MD: "Purchase Diovan - Quality online Diovan OTC".
The administration of folic acid during the first trimester may reduce the risk of neural tube defects purchase generic diovan on line blood pressure dizziness. CefIxIme 1 Prescription under medical supervision Therapeutic action – Third-generation cephalosporin antibacterial Indications – Typhoid fever in children – Acute cystitis in girls over 2 years 160 mg diovan for sale heart attack 2013 film, pregnant women and lactating women – Acute pyelonephritis in adults – Cervicitis and urethritis due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae (in combination with a treatment for chlamydia) Presentation – 200 mg tablet – 100 mg/5 ml powder for oral suspension buy cheap diovan 40 mg arrhythmia alcohol, to be reconstituted with filtered water Dosage – Typhoid fever in children Child over 3 months: 20 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses – Acute cystitis in girls over 2 years 8 mg/kg once daily – Acute cystitis in pregnant and lactating women, acute pyelonephritis in adult 400 mg/day in 2 divided doses – Cervicitis and urethritis due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae Child: 8 mg/kg as a single dose Adult: 400 mg as a single dose Duration – Typhoid fever: 7 days; acute cystitis: 3 days for girls and 5 days for adults; acute pyelonephritis: 10 to 14 days Contra-indications, adverse effects, precautions – Do not administer to patients with allergy to cephalosporins. Contra-indications, adverse effects, precautions – Do not administer in case of poisoning by caustic or foaming products, or hydrocarbons: risk of aggravation of lesions during vomiting (caustic products), aspiration pneumonia (foaming products, hydrocarbons), and airway obstruction due to foaming when vomiting (foaming products). Therapeutic action – Phenicol antibacterial Indications – Alternative to first-line treatments of bubonic plague – Alternative to first-line treatments of typhoid fever – Completion treatment following parenteral therapy with chloramphenicol Presentation – 250 mg capsule Dosage – Child from 1 year to less than 13 years: 50 mg/kg/day in 3 to 4 divided doses; 100 mg/kg/day in severe infection (max. In these events, stop treatment immediately; • gastrointestinal disturbances, peripheral and optic neuropathies. If used during the 3rd trimester, risk of grey syndrome in the newborn infant (vomiting, hypothermia, blue-grey skin colour and cardiovascular depression). In areas where resistance to chloroquine is high, chloroquine must be replaced by another effective antimalarial suitable for prophylactic use. Contra-indications, adverse effects, precautions – Do not administer to patients with retinopathy. Dosage – Child from 1 to 2 years: 1 mg 2 times daily – Child from 2 to 6 years: 1 mg 4 to 6 times daily (max. Contra-indications, adverse effects, precautions – Administer with caution and monitor use in patients with prostate disorders or closed-angle glaucoma, patients > 60 years and children (risk of agitation, excitability). Dosage – Acute or chronic psychosis Adult: initial dose of 75 mg/day in 3 divided doses; if necessary, the dose may be gradually increased up to 300 mg/day in 3 divided doses (max. Once the patient is stable, the maintenance dose is administered once daily in the evening. Duration – Acute psychosis: minimum 3 months; chronic psychosis: minimum one year. Contra-indications, adverse effects, precautions – Do not administer to patients with closed-angle glaucoma, prostate disorders; to elderly patients with dementia (e. Dosage and duration – Adult: 200 to 400 mg as a single dose if possible one hour before anaesthetic induction Contra-indications, adverse effects, precautions – May cause: diarrhoea, headache, dizziness, skin rash, fever. Remarks – Effervescent cimetidine can be replaced by effervescent ranitidine, another H2-receptor antagonist, as a single dose of 150 mg. The effervescent tablets containing sodium citrate have a more rapid onset of action, and can thus be used for emergency surgery. In the event of allergic reaction, severe neurological disorders, peripheral neuropathy or tendinitis, stop treatment immediately. Remarks – Capsules are not suitable for children under 6 years (risk of aspiration). Open the capsule and mix the content into a spoon with food or fruit juice to mask the unpleasant taste. Dosage – Adult: initial dose of 25 mg once daily at bedtime, then increase gradually over one week to 75 mg once daily at bedtime (max. Contra-indications, adverse effects, precautions – Do not administer to patients with recent myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, closed-angle glaucoma, prostate disorders. Treatment should be discontinued in the event of severe reactions (mental confusion, urinary retention, cardiac rhythm disorders); • psychic disorders: exacerbation of anxiety, possibility of a suicide attempt at the beginning of therapy, manic episode during treatment. Contra-indications, adverse effects, precautions – Do not administer to patients with acute respiratory depression or asthma attack. The newborn infant may develop withdrawal symptoms, respiratory depression and drowsiness in the event of prolonged administration of large doses at the end of the 3rd trimester. Monitor the mother and the infant: in the event of excessive drowsiness, stop treatment.
Epinephrine—A hormone with neurotransmitters made in the inner core of the adrenals that help you focus and problem-solve buy cheap diovan 160mg line blood pressure keeps spiking. It creates amounts of glucose and fatty acids that can be used by the body as fuel in times of stress or danger when increased alertness or exertion is required order diovan 40 mg otc heart attack move me stranger extended version. It is responsible for the growth of the womb (uterus) purchase diovan 40mg otc blood pressure upon waking, breast development, fallopian tubes, and vagina, and plays a role in the distribution of body fat in women. It is used to treat breast tenderness, cysts, cancer, fibroids, endometriosis, endometrial cancer, hot flashes, and symptoms in women who are experiencing or have experienced menopause. Fibromyalgia—A common syndrome in which a person has long-term, body-wide pain and tenderness in the joints, muscles, tendons, and other soft tissues. Fibromyalgia has also been linked to fatigue, sleep problems, headaches, depression, and anxiety. Free T3 (Free triiodothyronine)—A free T3 (fT3) test is used to assess thyroid function. It is ordered primarily to help diagnose hyperthyroidism and may be ordered to help monitor the status of a person with a known thyroid disorder. Free T4 (Free thyroxine)— The free T4 (fT4) test is thought by many to be a more accurate reflection of thyroid hormone function and aid in the diagnosis of female infertility. Glandular therapy—A technique that is useful to treat hormonal problems by alternative healers but lacks randomized trial data. Generally the historical motive was to support the weak gland of the patient with an analogous animal gland rich in specific nutrients. Glucocorticoids—Made in the outside portion (the cortex) of the adrenal gland, glucocorticoids regulate the metabolism of glucose and are chemically classed as steroids. Hawthorne effect—The phenomenon in which subjects in behavioral studies change their performance in response to being observed. Hippocampus—The main home for memory formation and storage in the brain, found under the frontal part of the cerebral cortex. It is the brain region responsible for memory, with its high number of cortisol receptors. Hyperarousal—The scientific term for “stressed out,” meaning that the body’s alarm system never shuts off. Hypercortisolism—Known as Cushing’s syndrome, hypercortisolism is a disorder that occurs when your body is exposed to high levels of the hormone cortisol. It can also occur if you take too much cortisol or other steroid hormones precursors. Hyperplasia may be a sign of abnormal or precancerous changes, particularly atypical hyperplasia of the endometrium. Blood pressure is a measurement of the force against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood through your body. Hypervigilance— Abnormally increased arousal, responsiveness to stimuli, and scanning of the environment for threats. Hypocortisolism—Also known as low cortisol, hypocortisolism occurs when your adrenal glands are unable to make a normal amount of the main stress hormone, cortisol. Hypoglycemia—The depletion of feel-good neurotransmitters that occurs when your blood sugar (glucose) is too low. Hypopituitarism—When the pituitary does not make normal amounts of some or all of its hormones— including the hormones that control the ovaries, thyroid, and adrenals—as a result of head injury, brain surgery, radiation, stroke, or a problem called Sheehan’s syndrome, which is when a woman bleeds severely during childbirth. Hypothalamus—An area of the brain that produces hormones that control body temperature, hunger, moods, sex drive, sleep, and the release of hormones from many glands, especially the pituitary gland.
Buy discount diovan on-line. Nephron Function.
Because the charges are separated across only the very small thickness of the membrane cheap diovan 80mg with mastercard heart attack vegas, only a few thousand charges need move before the system reaches equilibrium discount 40mg diovan amex blood pressure age chart. Because a cell has trillions of K+ ions inside purchase diovan visa heart attack man, the concentration changes negligibly. However, if a cell is held in a non-equilibrium condition for a long period of time, the concentration gradients can eventually be dissipated. An important point, particularly with regard to resting membrane potentials in a multi-ion system, is that the resting potential, while stable, does not represent a true equilibrium condition. But in this case, the cell is at the equilibrium potential for neither ion, so neither ion is in equilibrium. In other words, at rest, there will be a steady flow of K out of the cell and a steady Nernst Potential and Osmosis - Daniel Madison, M. Thus, in order to maintain their ion concentration gradients over the long term, cells must employ active transport to move ions back into or out of the cell against their concentration gradients. Here are some real concentration numbers for a cell (in mM): Inside Outside An- 131. For purposes of this calculation, you can use the simplified version of the Nernst equation: [ion ]i E ion 61. Assuming a cell with permeabilities for Na of 2, K of 20 (assume all other ions to be impermeant), and the concentrations listed above, where what would the resting potential of this cell be? Clarify the functional implications of current flow from one heart cell to the next C. Become acquainted with the normal pathway for impulse spread through the heart Cardiac action potentials serve many purposes. They form the cellular basis for pacemaker activity, impulse spread and control of cardiac contraction. Despite this variety of functions, there are ample reasons for believing that impulses in cardiac cells follow the same principles as in other excitable tissues. Thus, your knowledge of neuronal excitability from the Neurobiology Course will provide a useful foundation for understanding action potentials in heart. We shall draw upon such similarities while focusing on unique aspects of cardiac activity. One characteristic of nerves is that a single axon in a whole nerve may be stimulated intracellularly and there will be no excitation in any of the other nerve fibers. The muscle fibers are not electrically coupled, and this arrangement permits considerable flexibility in allowing the central nervous system to specify the strength or temporal pattern of the whole muscle action. If a strip of quiescent heart muscle is dissected and stimulated locally, the entire piece of tissue will actively contract. The all-or-nothing law applies in that there is either a full contraction or none at all. Despite its multi-cellular structure, we still speak of heart muscle as a functional syncytium since an action potential spreads electrically to all of the individual cells in the tissue. Electron-microscope studies have provided a likely candidate for the low resistance pathway between cardiac cells: a region where the membranes of two adjacent cells are in very close opposition (see figure). This morphological specialization has the appearance of a spot weld, and has been termed the gap junction. The actin (thin) filaments insert into the fasciae adherentes at the end of the cell. There is good circumstantial evidence that the gap junction is the pathway for intercellular current flow. Thus, conduction may be reversibly blocked by increasing the tonicity of the external solution, and this effect occurs in parallel with a separation of the cells at the gap junction.
At physiological pH purchase generic diovan canada heart attack demi lovato mp3, however cheap 80mg diovan fast delivery blood pressure chart what your reading means, these amines are likely to be protonated and to occur in rigid ring structures discount diovan 80mg mastercard arrhythmia vs dysrhythmia. Although it is rather dangerous to assign a definite distance between the -onium and ester groups (estimated at about 0. If the ethylene is branched, only methyl groups are allowed, as shown in the muscarinic agonist methacholine (4. The only useful replacement for the acetate has been a carbamate group, resulting in carbachol (4. Cyclization is a good drug design strategy in that in constrains conformational flexibility, thereby increasing receptor specificity. However, this is merely a general approximation, for although the muscarinic activity is quite specific, steric parameters are rather irrelevant to the action of nicotinic agonists. In muscarinic agonists a third binding point, involving the methyl group of the acetate, may assume increased significance. Whereas the primary structural requirements for nicotinic agonists are a quaternary ammonium and a carbonyl group, the muscarinic agonists are characterized by an ammonium and a methyl group. The carbonyl group is the primary hydrogen- binding site in both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. Cholinergic agonists (cholinomimetics) enjoy widespread use in the treatment of gastrointestinal and urinary tract problems. In clinical problems involving reduced smooth muscle activity without obstruction, cholinomimetics with muscarinic effects may be of use. These clinical problems include postoperative ileus (bowel paral- ysis following its surgical manipulation) and urinary retention (bladder atony, either postoperatively or secondary to spinal cord injury [the so-called neurogenic bladder]). A heart attack (especially one affecting the inferior wall of the heart) may depress the electrical system of the heart, impairing cardiac output. The judicious parenteral use of atropine or some other antimuscarinic agent may be of value in increasing the heart rate. Antimuscarinics are widely used for gastrointestinal and genitourinary indications. In the treatment of simple traveler’s diarrhoea (or other mild, self-limited gastrointestinal hypermotility conditions) antimuscarinics provide rapid relief; frequently they are combined with an opioid drug (see chapter 5), which has an additive antiperistaltic effect on bowel motility. Atropine has been used to treat urinary urgency associated with bladder inflammation; oxybutynin (4. Finally, anticholinergics have been used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (section 4. The oldest anticholinergics are the tropane alkaloids of Atropa belladonna (night- shade). Atropine is the racemate of (−)hyosciamine, whereas scopolamine has an epoxide ring. In large doses, all of these anticholinergic agents have central excitatory and hallucinogenic effects and were prominent in medieval “witches’ brews. Although ganglia are, functionally, normal receptors, they probably differ structurally from the receptors at the neuromuscular endplate, and show different accessibility. Ganglionic and neuromuscular blocking agents are therefore two structurally different groups of anticholinergic drugs. However, because none of these compounds can dis- tinguish sympathetic from parasympathetic ganglia, they have numerous side effects. Consequently, they have largely been replaced by the more selective β-adrenergic blocking agents. They are capable of relax- ing the abdominal muscles without the use of deep anesthesia, and make surgery much easier for both the surgeon and the patient. These agents were developed through the study of curare, the arrow poison of South American Indians.