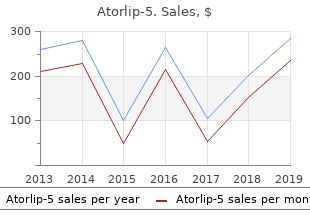
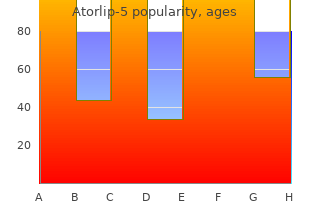
Atorlip-5
University of San Diego. V. Rakus, MD: "Order Atorlip-5 - Discount online Atorlip-5 OTC".
Patients who are willing to accept modest improvements and desire short visits with little to no downtime postprocedure are best suited to treatment with nonfractional lasers (Table 1) buy atorlip-5 5mg free shipping cholesterol lowering eating plan south africa. Patients with mild to moderate wrinkles seeking more dramatic reduction of wrinkles purchase generic atorlip-5 canada cholesterol levels nursing mothers, who are willing to accept some procedural discomfort and postprocedure downtime cheap 5mg atorlip-5 cholesterol medication types, are good candidates for fractional lasers. Patients with severe wrinkling are better candidates for ablative lasers or surgery, especially if skin laxity is significant. While, fractional lasers that target water are also indicated for darker skin types, these technologies have greater risks of pigmentary alterations and may necessitate more conservative settings which can attenuate results. Patient Expectations Skin resurfacing with nonablative lasers requires a series of treatments performed at monthly intervals to demonstrate visible results: 4–6 for fractional lasers and 6–8 for nonfractional lasers. Results with nonablative resurfacing treatments (even with a series) are slow and subtle compared to ablative lasers (see Chapter 6). Assessment of patients’ expectations at the time of consultation and commitment to a series of treatments is essential to ensure success with these treatments. Results are typically seen 2–3 months after the initial laser treatment, and improvements may continue up to 6 months posttreatment. However, these treatments have the advantage of requiring little to no recovery time, lower risks of complications, and are easily incorporated into patients’ daily lives. Fractional lasers that target water have faster results and more significant improvements than nonfractional lasers. Results are usually seen by 1 month posttreatment and, like nonfractional lasers, improvements may continue up to 6 months posttreatment. These laser treatments are more uncomfortable than other nonablative lasers and typically require topical anesthetic preprocedure and forced-air cooling during the procedure for treatment to be tolerable. Postprocedure erythema and edema typically last for 3–4 days, and procedures can be associated with complications such as pigmentary alteration, acne exacerbations, and milia formation. Indications • Mild static rhytids • Rough skin texture • Enlarged pores • Superficial acne scars Additional Indications for Nonablative Fractional Lasers • Moderate static rhytids • Benign pigmented lesions (e. These more aggressive, deeper skin resurfacing procedures offer greater potential for static wrinkle reduction, but require longer recovery times and have greater risks of complications. Although fractional lasers have reduced recovery time and risk of complications, ablative laser treatments, whether fractional or nonfractional, create an open wound and have risks of scarring and infection. Nonlaser treatment options for wrinkle reduction include superficial skin resurfacing with light chemical peels or microdermabrasion, and topical skin care products such as retinoids and exfoliants (e. Other available treatments for facial lines and wrinkles include botulinum toxin for dynamic wrinkles and dermal fillers for static lines, and these treatments are often performed in conjunction with laser procedures. While these light-based devices have similarities to lasers and other light-based technologies, their results are extremely modest and are briefly discussed here. They do not operate based on the theory of selective photothermolysis, but rather are based on the principle of photomodulation, where cellular activity is modulated through illumination by particular wavelengths of light. Reduction of skin laxity and folds to improve skin contour is commonly known as “skin tightening”; however, the term used by the U. Radiofrequency devices (such as Thermage, Solta) employ® rapidly alternating current that creates heat when applied to the skin due to the skin’s resistance to current flow. Tissue heating with radiofrequency devices is controlled by several factors, including the type of electrodes used (e.

Furthermore buy atorlip-5 5mg lowest price cholesterol test results vary, in acute situations in which supplemental oxygen is necessary to maintain adequate tissue oxygenation generic atorlip-5 5mg visa cholesterol medication causing joint pain, it should not be with held even if there is a risk that ventilatory support may be required buy atorlip-5 5mg line high cholesterol medication side effects. Based on studies demonstrating that breathing enriched oxygen mixtures limited infarct size in animals, it has become common practice to administer oxygen to patients suspected of experiencing ischemic-type chest discomfort [84]. The routine use of supplemental oxygen, however, may be associated with an increased risk of death, questioning this practice [86,87]. Supplemental oxygen protects against hypoxemia resulting from pulmonary vasodilation induced by β agonists and minimizes hypoxemia-induced vasoconstriction [89]. Normal levels of oxygen (normoxia) may protect against cardiac arrhythmias and may also help oxygen delivery to peripheral tissues [3]. The National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Expert Panel Report 3 recommends oxygen administered via nasal cannula or mask to maintain an SaO greater than 90% (greater than2 95% in pregnant women and in patients with a history of heart disease) [13]. Normoxemic hypoxia encompasses conditions that are characterized by the potential or actual documentation of tissue hypoxia but with a normal PaO [2 84]. Tissue hypoxia occurs as a result of abnormal hemoglobin function, deficient delivery, or inefficient use of oxygen by the tissues. Examples of such conditions include acute anemia, carboxyhemoglobinemia (perhaps the most lethal), and sickle-cell crisis. Recommendations for the use of supplemental oxygen for normoxemic hypoxic conditions are outlined as follows: 1. Although the definitive treatment is sufficient blood replacement, supplemental oxygen is a reasonable temporizing measure. This should be given immediately and without interruption until it is verified that carboxyhemoglobinemia has fallen to less than 5%. Although hyperbaric oxygenation represents a potentially more effective alternative, it is not readily available for most patients. If it is available, patients with carboxyhemoglobin levels greater than 40% or with cardiac or neurologic symptoms should be considered for immediate transportation to a hyperbaric oxygen facility for treatment. Because deoxygenation makes cells sickle, however, it seems reasonable to give supplemental oxygen in this setting. Because of the risk of oxygen toxicity, concentrations in excess of 50% should not be given for more than 48 hours. Several trials have shown that oxygen delivered at rates between 6 and 12 L per minute can reduce acute pain from cluster headaches [91]. Routine perioperative administration of supplemental oxygen, regardless of the patient’s SaO,2 may be advantageous in reducing the incidence of postoperative surgical site infections. An increase in the alveolar-arterial partial pressure of oxygen [P(A-a)O ] gradient and a decrease of the functional2 residual capacity are common perioperatively and postoperatively. Ventilation–perfusion abnormalities and intrapulmonary shunting may occur, and while generally corrected within the first few hours after most types of surgery, it may be more significant among the elderly, the obese, for patients with pre-existing cardiopulmonary conditions, and after surgery of the upper abdomen and thorax. Because the PaO usually2 increases with the administration of supplemental oxygen, low concentrations of supplemental oxygen should be administered to those at risk of postoperative hypoxemia [93]. In some cases, lung-expansion maneuvers may be necessary after oxygen fails to correct the PaO [2 82]. Oxygen Delivery Systems In the acute setting, bulk supply systems are used as a relatively inexpensive means of oxygen delivery. Selection should be based on the amount of oxygen the system can deliver and its clinical performance. Factors capable of affecting performance include the type of device chosen, flow rates used by the device, the fit of the device, respiratory rate, inspiratory flows, and tidal volumes. Standard dual-prong nasal cannulas are the most commonly used oxygen delivery devices for administering low-flow oxygen. Nasal cannulas are easy to use, relatively comfortable, fairly unobtrusive, do not interfere with eating or talking, and relatively inexpensive.
Once the diagnosis is made and the causative drug is stopped buy 5 mg atorlip-5 overnight delivery cholesterol levels ldl vs. hdl, the pustules will resolve in less than 15 days with desquamation buy atorlip-5 5 mg overnight delivery cholesterol levels vegetarian diet, and prognosis is excellent generic 5 mg atorlip-5 visa cholesterol lowering diet plan menu. Antipyretics may be used for symptomatic treatment of the fever and topical steroids may be used for symptomatic treatment of the rash, although neither will hasten the resolution of the eruption. Although age at presentation varies with the underlying cause, patients are typically over 40 or 45 years. Male to female ratio and reported incidence are also variable, and there is no racial predilection [33–35]. The causes of erythroderma may be categorized into preexisting skin conditions (psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis), drug reactions, malignancy, skin infections and infestations, and idiopathic etiology [31,33]. Over 60 topical and systemic medications have been implicated in erythroderma, including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, anticonvulsants, penicillin, vancomycin, antifungals, and barbiturates [34,35]. Primary blood vessel malignancy and solid organ cancers are also reported in association with erythroderma [35]. Varying degrees of scaling, which often begin at flexural surfaces, follow intense widespread erythema within 2 to 6 days. Along with intense erythema, patients may have fever, hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles, nail dystrophy, cheilitis, alopecia, edema of the face and legs, dermatopathic lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, and splenomegaly [33,34]. Increased cutaneous blood flow results in exaggerated heat and fluid losses with a compensatory increase in the body’s basal metabolic rate. This, in conjunction with the shedding of 20 to 30 g per day of proteinaceous scale, can result in a hypoalbuminemia that exacerbates edema and nutritional deficits [34,35]. Complications include electrolyte imbalance, thermoregulation, dehydration, high output cardiac failure, and secondary infections. Identification of the underlying trigger is important in the evaluation and management of erythrodermic patients. Early examination of the skin with corroborating evidence from skin biopsy may be helpful in establishing the etiology, but in the majority of adult cases, the underlying dermatosis is obscured by widespread erythema and scaling. Skin biopsy has recently been shown to be more useful in detecting some underlying triggers for infantile and neonatal cases of erythroderma [36]. Initial treatment, regardless of the underlying cause, consists of temperature regulation (in spite of the skin being warm or hot to the touch, patients become hypothermic), hemodynamic support and monitoring, and skin care. Tap water–soaked gauze dressings may be changed every 2 to 3 hours, and tepid baths may provide additional relief. Systemic corticosteroids can be helpful, but must be used with caution in atopic dermatitis and are contraindicated in infection and psoriasis. Although it is now seen in multiple settings, it is still worthwhile to be sure that in menstruating women, a tampon has not been left in place. Pathophysiology of both entities involves massive release of cytokines due to bacterial toxins acting as superantigens. Skin biopsy shows a neutrophilic and eosinophilic perivascular and interstitial infiltrate with scattered necrotic keratinocytes. Cellulitis and Erysipelas Cellulitis is an acute bacterial infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissues. Erysipelas is a more superficial skin infection that involves the upper dermis and often superficial lymphatics. It is distinguished from cellulitis and other infections by its very sharply demarcated borders and induration.
The normal heart/pulse rates in the different age groups in children are given in Table 1 discount 5 mg atorlip-5 with mastercard cholesterol ratio nice. A large cuff will give an erroneously low reading while a small 1 year 30 cuff will give a high reading purchase atorlip-5 5 mg line cholesterol score of 220. Here the child’s arm is 10 years 18 raised and a tight bandage is applied up to the level of the cuff so as empty the blood from the upper limb cheap 5mg atorlip-5 amex cholesterol medication elderly. In younger children where auscultation at the Below 2 months 60 or more cubital fossa is difficult, the systolic reading obtained by 2 to 12 months 50 or more palpation may suffice. The Doppler technique of measuring 12 months to 5 years 40 or more blood pressure is more accurate and can be used in children, if available. For every pediatric examination, both the upper limb and lower limb pressures must be recorded to detect Table 1. Normally, the pressure recorded in the lower limbs Newborn 140 is about 10 mm Hg higher than the upper limbs. Reserve recording the pressure to the last in order not to irritate or 1 year 110 scare the child. Normal blood pressure readings in children 3 years 100 in the different age groups are given in Table 1. Normal 8 years 90 blood pressure is defined as systolic and diastolic pressure, 10 years 80 less than 90th percentile for that age and sex. Hypertension is defined as average systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure equal to or greater than the 95th percentile for that age than 150 per minute in infants and more than 120 per minute and sex, on at least three occasions. The Heart Association (Pediatric Advanced Life Support Course) radial and femoral pulse must be palpated simultaneously recommendations, a formula has been devised to calculate to look for any radio-femoral delay. Remember, the heart the 50th percentile of systolic pressure in children over the rate in a struggling or crying child will be more. The height can be measured for children more than 2 years old, weight of the child is also useful for calculating the right while for younger children, the recumbent length should be dosage of the drugs to be given. The child doubles its birth weight by 4 months, palsy, where the height or length could not be measured, triples it by 1 year and increases it 4 times by 2 years. For the length of various segments of the body are measured calculating expected normal weight, the formula shown in separately and added together to get the length. Weight is recorded on a weigh While measuring the height, it is also important to scale which should be frequently checked with standard measure the upper segment (from the vertex to the weights and zero error must be adjusted before weighing. The rate of growth of the height upper and lower segments varies with age as shown in Table the height of the child is a good indicator of the chronicity 1. Height is ideally measured using for that age may suggest the presence of specific growth Harpenden stadiometer. Stature should also be defined with wall with his bare feet touching each other, the heel, calf, parent’s height being taken into account, referred to as the buttock, upper back and occiput touching the wall and mid-parental height. The expected head circumference for the Mother’s height + (Father’s height-13) = age may be calculated from (Tables 1. For boys: Approximate projected adult height (in cm) Microcephaly is defined as head circumference, more than 3 standard deviations below the mean or less than the 5th (Mother’s height + 13) + Father’s height percentile for the age and sex. In the size of the head is a good indicator of the size of its the infant, the chest circumference is lesser than the head contents, viz. In undernutrition, the chest circumference is measured with a non-stretchable tape circumference remains lower than the head circumference passing through the maximum point of the external even beyond one and half years whereas in well-nourished occupational protuberance posteriorly and a point just above children, the chest circumference may exceed the head 12 the glabella anteriorly. It equals the height at 10 years, and after 10 years it is from 1 cm to 2 cm more than the height. A large number of accepted methods are arm span available for assessing development. Of this, the Gesse ll It is the distance between the tips of the middle fingers with developmental scale and the Bayley developmental scale both arms held wide open, i.