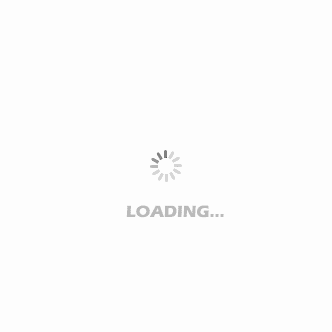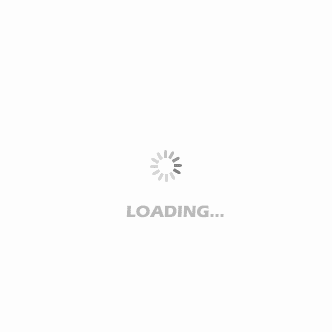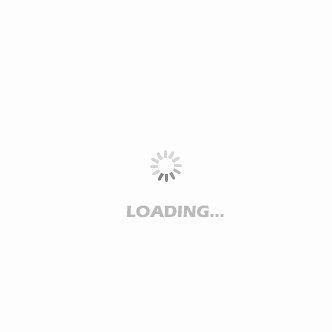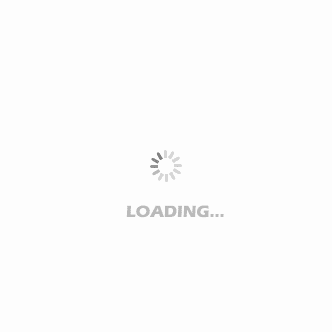
Crestor
Newberry College. D. Fraser, MD: "Order Crestor online no RX - Proven Crestor online no RX".
N-of-1 trial: A randomized trial in an individual to determine the optimum treatment for that individual crestor 10 mg cheap cholesterol medication diabetes. Noninferiority trial: A trial designed to determine whether the effect of a new treatment is not worse than a standard treatment by more than a prespecified amount purchase genuine crestor cholesterol levels targets. Nonrandomized study: Any study estimating the effectiveness (harm or benefit) of an intervention that does not use randomization to allocate patients to comparison groups order crestor uk kaiser cholesterol levels. There are many types of nonrandomized studies, including cohort studies, case-control studies, and before- after studies. Null hypothesis: The statistical hypothesis that one variable (for example, treatment to which a participant was allocated) has no association with another variable or set of variables. Number needed to harm: The number of people who would need to be treated over a specific period of time before one bad outcome of the treatment will occur. The number needed to harm (NNH) for a treatment can be known only if clinical trials of the treatment have been performed. Number needed to treat: An estimate of how many persons need to receive a treatment before one person would experience a beneficial outcome. Observational study: A type of nonrandomized study in which the investigators do not seek to intervene, instead simply observing the course of events. Odds ratio: The ratio of the odds of an event in one group to the odds of an event in another group. Off-label use: When a drug or device is prescribed outside its specific FDA-approved indication, to treat a condition or disease for which it is not specifically licensed. Outcome: The result of care and treatment and/ or rehabilitation. In other words, the change in health, functional ability, symptoms or situation of a person, which can be used to measure the Newer antiplatelet agents 68 of 98 Final Update 2 Report Drug Effectiveness Review Project effectiveness of care/treatment/rehabilitation. Researchers should decide what outcomes to measure before a study begins; outcomes are then assessed at the end of the study. Outcome measure: Is the way in which an outcome is evaluated---the device (scale) used for measuring. One-tailed test (one-sided test): A hypothesis test in which the values that reject the null hypothesis are located entirely in one tail of the probability distribution. For example, testing whether one treatment is better than another (rather than testing whether one treatment is either better or worse than another). Open-label trial: A clinical trial in which the investigator and participant are aware which intervention is being used for which participant (that is, not blinded). Random allocation may or may not be used in open-label trials. Per protocol: The subset of participants from a randomized controlled trial who complied with the protocol sufficiently to ensure that their data would be likely to exhibit the effect of treatment. Per protocol analyses are sometimes misidentified in published trials as intent-to-treat analyses. Pharmacokinetics: the characteristic interactions of a drug and the body in terms of its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Placebo: An inactive substance commonly called a "sugar pill. It does not contain anything that could harm a person.
Potential therapeutic applications of fructose-1 order crestor 20mg without a prescription cholesterol levels when breastfeeding,6-diphos- 2011;118(4):1109-1112 buy crestor in united states online cholesterol medication ezetrol. Inhaled carbon HQK-1001 cheap crestor 10mg mastercard cholesterol ratio less than 2, an oral fetal globin inducer, in sickle cell disease. Phase I study of eptifibatide 368 American Society of Hematology in patients with sickle cell anaemia. L-glutamine therapy non-ionic surfactant in the management of acute chest syn- reduces endothelial adhesion of sickle red blood cells to drome. Pathogenesis and clinical implications of HIV-related anemia in 2013 Amanda J. Redig1 and Nancy Berliner1,2 1Department of Medicine, and 2Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Anemia is a common feature of HIV-related disease and has been uniformly demonstrated to be an independent predictor of morbidity and mortality. Although anemia often responds to combination antiretroviral therapy, many patients remain anemic despite therapy and such persistent anemia continues to negatively affect prognosis regardless of drug response. We postulate that the pathophysiology of anemia in HIV, especially that which persists in the face of combination antiretroviral therapy, is a reflection of underlying proinflammatory pathways that are also thought to contribute to anemia in the elderly, as well as other age-related chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This suggests that HIV induces inflammatory pathways that are associated with a pattern of accelerated aging and that anemia is a biomarker of these processes. A better understanding of the pathophysiology of HIV-related anemia may provide important entry points for improving the chronic manifestations of HIV-related disease. Introduction hemoglobin concentration of 13 g/dL for men and 12 g/dL for Anemia is among the most common hematologic abnormalities in nonpregnant women. However, even while improving therapeutic options and disease management. Recent acknowledging differences in definitions, there is no doubt that emerging studies have also begun to suggest that there may be a anemia is a significant clinical challenge for the HIV population, connection between the underlying mechanisms driving the develop- because somewhere between 1. A growing body of data has established that HIV infection is associated with increased expres- A closer review of epidemiological data within this population sion of proinflammatory cytokines,2 including many of the same reveals several noteworthy trends. First, it appears that the degree of biomarkers previously associated with inflammation and anemia of anemia is correlated with HIV/AIDS disease progression in both aging. Because effective antiretroviral therapy (ART) has anemia and HIV stage. Furthermore, several studies in a range of dramatically increased the life expectancy of patients with HIV, patient cohorts demonstrated that anemia has prognostic signifi- improved understanding of the ways in which HIV infection alters cance for morbidity and mortality measures in HIV patients,7,8 physiologic parameters will be an important component of develop- supporting the possibility that the virus itself may play an indepen- ing targeted therapies to affect morbidity and mortality in this dent role in driving dysfunctional erythropoiesis. An number of patients in both adult and pediatric populations. However, when evalu- ity of the role played by anemia in this patient cohort, anemia has ating the large body of literature on this topic, it is important to note been associated with shortened median survival in HIV patients the various definitions used to clinically diagnose a patient with irrespective of their initial CD4 count. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines anemia as a demonstrates that when a range of potentially relevant demographic Hematology 2013 377 and clinical variables are considered, CD4 count and hemoglobin EPO were decreased. Once again, despite the widely diver- growth media for these studies suggests that the progenitor cells gent socioeconomic factors that characterize HIV worldwide, the from the HIV patients were intrinsically refractory to the growth degree of clinical anemia remains an independent risk factor for effects of EPO, resulting in accumulation of colonies at a relatively predicting mortality from HIV even upon initiation of therapy. However, after These findings identify anemia as an important variable in monitor- initiation of cART therapy, circulating levels of EPO and transferrin ing HIV disease progression and management, particularly in levels increased in patient serum, and the number of BFU-E resource-limited settings. These data also begin to suggest that colonies normalized compared with uninfected controls in ex vivo understanding the mechanisms by which HIV causes anemia may studies. The hema- Multifactorial pathogenesis of anemia in HIV topoietic stem cell may even be a reservoir for latent viral infection, There are several factors believed to contribute to the pathophysiol- although this remains controversial.
These new drug classes will bring about fundamental changes to current ART cheap 10 mg crestor cholesterol types. The dogma of always using two nucleoside analogs as the backbone of every therapy may start to change cheap crestor 20mg with amex cholesterol over 500. Many of the currently widespread drugs will disappear over the next few years order generic crestor line cholesterol test south africa. The end of HIVID, Agenerase, Fortovase or Viracept is just the beginning. Veteran agents like AZT, d4T, ddI, nelfinavir or indinavir are not recommended by guidelines anymore although they served us in HIV management in the nineties. Will we be needing saquinavir, fosampranavir or even efavirenz and lopinavir as much as we do today five years from now? A normal life expectancy seems realistic today with treatment. This will pose a tremendous challenge for patients, physicians and for the pharmaceutical industry and payors. The comfortable situation at present does not mean one can relax. There is uncertainty about whether our drugs can stand the test of time over decades. Effects on the heart, kidney, bones and other organs in an aging HIV population are difficult to foresee. If the cure is delayed, over the decades one will need a wider breadth and range of available drugs. It will not be easy for new drugs to be approved, as vicriviroc has shown. How do you show the advantages of a new drug over other successful ther- apies today? Approval for new drugs is becoming more strict and the market is tight- ening. Already one can observe the pharmaceutical industry’s caution. The days may be over when an HIV drug got from the laboratory to the market within five years. Compared to the previous decade, the HIV ARV pipeline is now drying up. At the same time, the simple question of “when to start” with ART has remained unanswered for a long time. Instead of David Ho’s recommendation from the nineties “hit hard, hit early”, we often heared “hit HIV hard, but only when necessary” (Harrington 2000) during the last decade. With the START study results appearing at the horizon, there is no doubt that this will change again. What roles do the following play: viral load, CD4 T cell changes, CD4 percentages, age, gender, host elements and viral tropism? These strategically important questions will hopefully find some answers through detailed analysis of the START study that are underway now.
Order crestor 20mg amex. *SALT and CHOLESTEROL* How To Be Studly! Myths of High Blood Pressure/ Dr Joe Wallace.
Randomized trial of estrogen plus progestin for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease in postmenopausal women proven 10mg crestor cholesterol lowering foods australia. Heart and Estrogen/progestin Replacement Study (HERS) Research Group purchase crestor on line cholesterol medication least side effects. Goldstein SR purchase crestor pills in toronto cholesterol food shrimp, Johnson S, Watts NB, Ciaccia AV, Elmerick D, Muram D. Incidence of urinary incontinence in postmenopausal women treated with raloxifene or estrogen. Johnson SR, Ettinger B, Macer JL, Ensrud KE, Quan J, Grady D. Uterine and vaginal effects of unopposed ultralow-dose transdermal estradiol. Venous thrombosis is not increased in younger women on genuine oestrogen postmenopausal hormonal replacement therapy: results from the Danish Osteoporosis Prevention Study (DOPS). Langer RD, Landgren BM, Rymer J, Helmond FA, Investigators O. Effects of tibolone and continuous combined conjugated equine estrogen/medroxyprogesterone acetate on the endometrium and vaginal bleeding: results of the OPAL study. Body mass index does not influence response to treatment, nor does body weight change with lower doses of conjugated estrogens and medroxyprogesterone acetate in early postmenopausal women. Hormone therapy Page 72 of 110 Final Report Update 3 Drug Effectiveness Review Project 200. Nelson HD, Humphrey LL, Nygren P, Teutsch SM, Allan J. Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy: Scientific review. Hormone replacement therapy and risk of venous thromboembolism: System evidence review. De Lignie & grave, De Vathaire B, Fournier FS, et al. Combined hormone replacement therapy and risk of breast cancer in a French cohort study of 3175 women. JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association. Resnick SM, Coker LH, Maki PM, Rapp SR, Espeland MA, Shumaker SA. Postmenopausal hormone use and cholecystectomy in a large prospective study. Hormone replacement therapy and endometrial cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Menopausal hormone replacement therapy and risk of ovarian cancer. Estrogen replacement therapy and ovarian cancer mortality in a large prospective study of U. Cancer incidence and mortality tin women receiving estrogen and estrogen-progestin replacement therapy - long term followup of a Swedish cohort. Long term hormone therapy for perimenopausal and postmenopausal women [Systematic Review]. Hormone therapy Page 73 of 110 Final Report Update 3 Drug Effectiveness Review Project Appendix A. Literature search strategies Menopausal Symptoms 1 DIENESTROL/ or dienestrol. Abbreviations and acronyms BMC=Bone mineral content BMD = Bone mineral density Ca = Calcium CCT = Combined continuous treatment regimen CEE = Conjugated equine estrogen Cyclic = Cyclic regimen DB = Double blind E2 = Estradiol E2V=Estradiol valerate EE= Esterified estrogen IU = International Unit MPA = Medroxyprogesterone acetate NETA = Norethindrone acetate NR = Not reported P = Placebo group RCT = Randomized controlled trial Rx = Treatment group SD = Standard deviation TAHBSOO = Total abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy Hormone therapy Page 76 of 110 Final Report Update 3 Drug Effectiveness Review Project Appendix C.