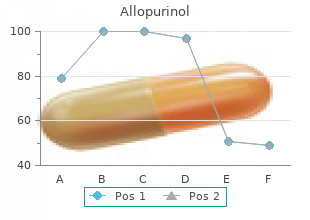
Allopurinol
Western Connecticut State University. S. Shakyor, MD: "Order cheap Allopurinol online no RX - Quality Allopurinol OTC".
The risk ratio is used in assessing the likelihood that an association represents a causal relationship buy allopurinol online pills gastritis natural supplements. For example purchase allopurinol 300mg amex gastritis or ulcer, the risk ratio of lung cancer in long-term heavyf smokers compared with non-smokers is approximately 20 order allopurinol in united states online gastritis celiac. This is very high and indicates that this relationship is not likely to be a chance finding. Of course, smaller risk ratios can also indicate a causal relationship, but care must be taken to eliminate other possible explanations (see Chapter 5). Attributable risk Attributable risk is the rate (proportion) of a disease or other outcome in exposed individuals that can be attributed to the exposure. This is a more useful term for public health purposes as it reflects the amount, usually expressed as a percentage, by which the risk of a disease is reduced by elimination or control of a particular exposure. Using attributable risk, it is possible to estimate the number of people spared the consequences of exposure, by subtracting the rate of the outcome (usually incidence or mortality) among the unexposed from the rate among the exposed in- dividuals. For example, if there were 6 deaths per 100 among smokers, and 1 death per 100 in non-smokers, the attributable risk would be 5 per 100. This assumes that causes other than the one under investigation have had equal effects on the exposed and unexposed groups. What are the possible explanations for the variation in diabetes prevalence rates indicated in Table 2. Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease in the Young of the American Heart Association. The Minnesota code manual of electro- cardiographic findings: standards and procedures for measurement and classification. Myocardial infarction redefined— a consensus document of the Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology Committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. Global estimates for prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance in adults. Counting the dead and what they died from: an assessment of the global status of cause of death. Sample registration of vital events with verbal autopsy: a renewed commitment to measuring and monitoring vital statistics. The Commission on Social Determinants of Health: Tackling the social roots of health inequities. Capacity building for an integrated noncommunicable disease risk factor surveillance system in developing countries. Comparative Quantification of Health Risks: Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors. Observations and experiments Epidemiological studies can be classified as either observational or experimental. The most common types of study are listed with their alternative names and units of study in Table 3. Observational studies Observational studies allow nature to take its course: the investigator measures but does not intervene. They include studies that can be called descriptive or analytical: x A descriptive study is limited to a description of the occurrence of a disease in a population and is often the first step in an epidemiological investigation.
This leaves changes in the radius of the blood vessels as the main contributor to variable resistance in the systemic circulation purchase allopurinol 100 mg overnight delivery chronic gastritis with hemorrhage. Thus cheap allopurinol 100 mg line gastritis diet natural, a small change in the radius of a tube will have a large effect on the flow of a liquid through that tube order 300mg allopurinol otc gastritis diet 90. Thus, veins serve as a blood reservoir, as well as transport passage back to the heart. Smaller veins converge into fewer but larger radii vessels, the velocity of blood flow increases as the blood moves toward the heart. Veins also serve as a large blood reservoir and because their storage capacity, they are called as “capacitance vessels”. As they have abundant collagen tissue, veins have little elasticity in comparison to arteries. Because of these properties, veins are highly distensible or stretchable, and have little elastic recoil. They distend well to accommodate additional amount of blood with only a little rise in venous pressure. Veins with extra amount of blood simply stretch to accommodate without tendency to recoil. When demands for blood are low, the veins can store extra blood as ‘reserve’, because of passive dispensability. As per Frank- Starling’s Law, increased venous return induces an increase in stroke volume of the heart. Therefore, a balance exists between the capacity of the veins, the extent of venous return, and the cardiac output. If more blood remains in the veins instead of being returned to the heart, such storage reduces the effective circulating volume. On the contrary, if venous capacity reduces, more blood returns to the heart, and continues circulating. Venous return refers to the volume of blood entering each atrium per minute from the veins. Since atrial pressure is ‘0’ mm Hg, a small but adequate driving force/pressure promotes the blood flow through large diameter and low resistance veins. Most of these factors influence the pressure gradient between the veins and the heart. Effect of Sympathetic Activity on Venous Return Veins are less muscular, have little muscle tone, but venous smooth muscles are richly supplied with sympathetic adrenergic vasoconstrictor fibers. Sympathetic stimulation produces venous vasoconstriction, elevating venous pressure, which in turn increases the pressure gradient to drive more blood from the veins into the right atrium. Less blood coming from the capillaries remains in the veins but continues to flow toward the heart. It is to be noted that arteriolar vasoconstriction reduces blood flow through these vessels, whereas venoconstriction increases flow through these veins, because of reduced capacitance, squeezes out more of the stored blood in the veins, thus increasing blood flow. This blood pumping action is known as the ‘skeletal muscle pump’, returning extra blood stored in the veins to the heart, during exercise. In exercise, venoconstriction and sympathetic activity also accompanying exercise, further enhances venous return.
Pathogenesis: ¾ Following colonization of small intestine order allopurinol in united states online gastritis peptic ulcers symptoms, the organism releases a potent enterotoxin called cholera toxin cheap allopurinol 300 mg amex gastritis diet ulcerative colitis. Clinical features: ¾ After an incubation period of 24 – 48 hours buy genuine allopurinol on line gastritis diet �����, patients experience sudden onset of profuse watery diarrhea accompanied by vomiting. Escherichia coli Infection There are different strains of Escherichia coli which give rise to diarrhea by different mechanisms: 23 1. Clinical Features: the clinical features are watery diarrhea without mucus or blood and abdominal cramps. Clinical Features: the clinical features include initial watery diarrhea followed by grossly bloody diarrhea and significant abdominal pain. Clinical Features: Produces a clinical disease that shares many features of Shigella infection (9). Brucellosis Pathogenesis: the organism invades the blood stream and localizes in the liver, spleen, bones, etc. Patients may appear well or may be very ill with any of the following manifestations: pallor, lymphadenopathy, enlarged liver and spleen, evidences of joint inflammation, rash, etc. Anthrax Pathogenesis: the organisms release anthrax toxin, which is responsible for the different manifestations of the disease. Cutaneous anthrax (95%), which is the most common characterized by localized skin lesion with black central eschar of necrosis and non-pitting edema. Inhalation anthrax (Wool sorter’s diseases) characterized by hemorrhagic mediastinitis with high mortality rate. Gastrointestinal anthrax, which is common in Ethiopia, and has high mortality rate. Since gastrointestinal anthrax is the most important form of anthrax with respect to acquisition through contaminated food, the following discussion focuses on this form of anthrax. Clinical features of gastrointestinal anthrax: There are two major forms: ¾ Gastrointestinal anthrax manifesting with fever, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, massive and/or bloody diarrhea and occasional ascites. Parasitic Food Borne Infections Most common food-borne parasitic diseases to be considered are Amebiasis, ascariasis, taeniasis and giardiasis. Amebiasis Pathogenesis: Motile trophozoites released from ingested cysts invade large bowel mucosa and cause mucosal ulcerations; they may also spread to other organs via the bloodstream to cause metastatic lesions (most commonly in the liver). Clinical features There are various clinical syndromes ¾ Symptomatic intestinal amebiasis manifests with abdominal pain and mild diarrhea followed by diffuse abdominal pain, weight loss, malaise, and bloody-mucoid diarrhea. Giardiasis Pathogenesis: ¾ Ingested cysts release trophozoites in the small intestine. But in symptomatic individuals, the clinical features range widely and include diarrhea, abdominal pain, flatulence, anorexia, weight loss, nausea and vomiting. Taeniasis Saginata Pathogenesis: ¾ This is the common form of taeniasis in Ethiopia. Clinical features: Patients notice passage of proglottids in the feces, perianal discomfort, abdominal discomfort or mild pain, nausea and anorexia. Clinical Features: ¾ Intestinal infection may be asymptomatic or may manifest with epigastric discomfort, nausea, hunger sensation, diarrhea, etc. Ascariasis Pathogenesis: ¾ Eggs released with feces mature in the soil and become infective in weeks. Clinical features: Clinical manifestations result from: ¾ Larval migration in the lungs: cough, shortness of breath, blood-tinged sputum ¾ Effect of adult worms in the intestine: usually asymptomatic, but may produce intestinal obstruction, perforation; or worms may migrate to ectopic sites to produce other manifestations like biliary colic. Viral Food Borne Infections Different viruses may be transmitted via contaminated food; most produce mild self- limiting illness, but occasional severe illnesses and even deaths may also occur. Viral gastroenteritis Pathogenesis: ¾ Rota virus causes osmotic diarrhea due to nutrient malabsorption.