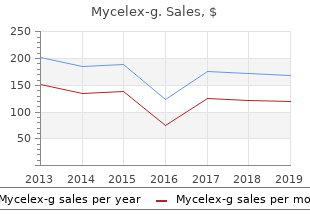
Mycelex-g
Cottey College. D. Kent, MD: "Order cheap Mycelex-g - Discount Mycelex-g online".
We have than chronically infected joints that contain thick pu- had success with septic tarsal joints in adult cattle by rulent debris buy mycelex-g overnight fungus edh deck. In acute infections discount 100 mg mycelex-g with amex fungus fly, joint lavage is the key simply inserting a surgical drain with the use of a Buhner to successful management 100 mg mycelex-g for sale fungus brutal plague inc. The infected joint should needle after ensuring that the entry and exit points are be surgically prepared and lavaged by through- sufciently large for drainage around the tubing. Blood or plasma transfu- involves arthrocentesis with a 14-gauge sterile needle sions and umbilical resection may be required to pre- followed by distention of the joint capsule and subse- vent further joint seeding. Exogenous wounds and other quent joint puncture by a second 14-gauge needle at sites of sepsis must be treated if they are thought to be the opposite side of the joint. Repeated joint lavage or arthrotomy squeezing as much uid out of the needles as possible. In calves, chronic infections, usually caused by injected into the joint or added to the lavage solution A. Open lavage of the joint coupled with sys- The history may suggest improvement while on antibi- temic antibiotics and physical therapy to prevent ten- otics, but recurrence of the lesion follows cessation of don contracture follow arthrotomy. Affected animals may be slightly lame and re- may be as simple as manipulation or may necessitate sist palpation of the affected area of bone. Most lesions splints or casts for support and immobilization in the involve the metatarsus or metacarpus. Calves are more likely to recover Diagnosis is conrmed by radiographs of the area. Field removal of a sequestrum is not difcult empiric because little documentation of effective reso- with the aid of radiographs and a bone-cutting chisel. In There is frequently signicant cancellous bone surround- districts where uoroquinolones are registered for cattle, ing the sequestrum, which must be removed before the they appear to be the rst choice. In addition to radiographs, newer macrolides such as tulathromycin are probably culture and sensitivity of the purulent discharge should the best choice for nonlactating cattle. Prognosis always should be guarded but is better for Long-term antibiotic therapy (4 to 6 weeks) is usually acute than chronic cases, better for single joints than required for osteomyelitis. Therefore the animal s value multiple ones, and better when the primary etiology must be sufcient to warrant the costs of therapy. Spastic Paresis, Spastic Syndrome Osteomyelitis and Bone Sequestra Spastic paresis is a rare, progressive muscular disorder Both of these conditions usually result in chronic or that causes overextension of the hind limbs secondary to recurrent purulent drainage from the skin overlying a spastic contraction of the gastrocnemius muscle. In some instances, soft both hind limbs may be involved, and affected cattle tissue swelling precedes drainage of pus and formation have very straight hind limbs with overextension of the of a stula originating at the necrotic or infected bone. In Holstein calves, spastic paresis has been called Elso heel because the condition tends to appear in ani- mals whose genealogy dates back to a bull called Elso. In the early stages, the leg may relax or intermittently re- lax following the gastrocnemius contraction that occurs after the animal rises. The calf also may raise its head and neck upward when showing overextension of the limb. Because of the progressive nature of the problem, if both hind limbs are affected, the calf is in extreme pain be- cause of gastrocnemius cramping or spasticity and even- tually will lose weight and prefer lying down to standing. When forced to stand, the affected limbs are held back rigidly in extension caudal to the body, and the gait is stiff because of difculty advancing the limb.
Diseases
- Follicular atrophoderma-basal cell carcinoma
- Goldblatt Viljoen syndrome
- Cryptomicrotia brachydactyly syndrome
- Neuropathy sensory spastic paraplegia
- Cote Adamopoulos Pantelakis syndrome
- Hay Wells syndrome
- SCARF syndrome
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type II Hunter syndrome- severe form
Exercise intolerance with or without dyspnea having abdominal disorders that lead to metabolic 4 cheap mycelex-g 100mg amex fungus worm. Ascites with or without pleural uid gers atrial brillation in cattle with normal hearts buy genuine mycelex-g line antifungal medication for dogs. Atrial brillation is ential diagnoses involves diseases that result in hypo- associated with irregular intensity of heart sounds discount mycelex-g generic fungi vs parasite. Hypoproteinemia also causes ventral pulse decit may be present in any cow with a rapid or edema and may cause exercise intolerance and tachy- irregular cardiac rhythm, especially when the rate ex- cardia. Echocardiography Two-dimensional echocardiography and Doppler echo- cardiography have greatly enhanced our ability to assess cardiac function and visualize anatomic variations and pathologic lesions in cattle. In short, echocardiography is now an es- Therefore venous distention and pulsation coupled sential component of a cardiology workup. B, Sinus from the thoracic inlet; and the ground electrode is at- bradycardia with heart rate of 36 beats/min recorded tached to the neck or withers. From any time from birth to 4 years of age but are more com- the same window, all four heart valves can be visual- mon in calves less than 3 months of age. Other signs of white muscle disease such as stiffness, difculty in pre- hension or swallowing, inhalation pneumonia, and myo- globinuria may or may not be present. Dyspnea may be directly related to the cardiac lesions or may be caused by Zenker s degeneration in the diaphragm or intercostal muscles. Tachycardia ( 120 beats/min) and arrhythmias are the most common specic cardiac signs, but murmurs may be present as well. If the heart is the only muscle involved, serum enzymes may not be greatly elevated; however, the heart seldom is the only area involved. Concurrent acute diarrhea, are recumbent, dehydrated, and have aspiration pneumonia would require intense antibiotic bradycardia or arrhythmia should be suspected of being therapy. Obviously only an acid-base and electro- at 72-hour intervals for three or four total treatments. Herd selenium status and preventive measures to address However, these may not be available in the eld. Calves that survive for consequences of underestimating the life-threatening 3 days following diagnosis have a good prognosis. Calves suspected to be hyperkalemic based on his- Hyperkalemia tory, physical signs, and arrhythmia or bradycardia Cardiac arrhythmias or bradycardia associated with should receive alkalinizing uids and dextrose. Being hyperkalemia is primarily observed in neonates having neonates, hypoglycemia may contribute to bradycardia severely acute diarrhea. Rotavirus or coronavirus 1 to 3 L is necessary, depending on the magnitude of the also may be involved in calf diarrhea, but they seldom metabolic acidosis and bicarbonate decit. This may gradually (with further elevation in potassium and fur- be true even in the acute phase of disease, but when ther reduction in resting membrane potential) the cells serum K is 5. Atrial standstill characterized by bradycardia and absence of P waves Congenital Heart Disease may occur and has been documented in association with hyperkalemia in diarrheic calves. Patent ductus arteriosus, which is rare as a the peaked T waves and attening of the P waves is very single defect in calves, can cause a systolic or continu- apparent. Prognosis for most is hopeless because of heart defects are eventually examined by a veterinarian eventual respiratory difculty and stunting. However, because of persistent or recurrent respiratory signs or calves do, in rare instances, survive to productive adult generalized ill thrift. The genetics of these multiple defects (eye, tail, the form of pulmonary edema associated with heart and heart) have not been investigated in Holsteins but failure and shunts or be caused by opportunistic bacte- have been assumed to be a simple recessive trait in rial pneumonia secondary to pulmonary edema and Guernseys. Usually only one calf is affected, thus mak- may lead to polycythemia secondary to hypoxia.
Syndromes
- Nausea and breast tenderness, which are less severe than with birth control pills or patches
- Esophageal spasm
- With general anesthesia, you are asleep and feel no pain.
- Epanutin
- Severe throat pain
- If you are or could be pregnant
- Immunodiffusion test
- Drink plenty of fluids.
Medically for prevention of urinary and faecal incontinence in recognized urinary incontinence and risks of adults discount mycelex-g 100mg amex anti fungal bacterial cream. The prevalence of potentially remediable pelvic muscle exercises in the early management of urinary incontinence in frail older people: a study using urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy purchase mycelex-g 100 mg antifungal examples. Prevalence and risk factors of incontinence the management of urinary incontinence in adults buy mycelex-g 100 mg overnight delivery antifungal topical. Prevention and treatment of education on duration and degree of incontinence after incontinence after radical prostatectomy. Pelvic foor rehabilitation is effective in patients with patterns of urinary incontinence in noninstitutionalized multiple sclerosis. Muscarinic receptor antagonists in the management for post prostatectomy urinary treatment of overactive bladder. Impact of early Short-term electrical stimulation: home treatment for pelvic foor rehabilitation after transurethral resection of urinary incontinence. Although the functioning evolves as the child progresses through majority of these outpatient visits cannot be classifed the frst several years of life and is heavily infuenced by underlying disease process, nocturnal enuresis is a by social, cultural, and environmental factors. Of the commercially insured children seen for Development of Voiding Control incontinence in the outpatient setting, 75% were 3- to In the infant, normal micturition occurs via a 10-year-olds, and 15% to 20% were 11- to 17-year- spinal-cord-mediated refex. Only 2% to 3% of the outpatient visits were it surpasses an intrinsic volume threshold, which made by children under the age of 3, in whom urinary results in a spontaneous bladder contraction. In the infant, the volume threshold for inpatient care, the average length of stay is between 5 urination is low; the infant voids approximately 20 and 7 days, and the length of stay appears to be even times per day (1). Fewer than As the infant develops and neural pathways 10 of every 100,000 visits for incontinence in children in the spinal cord mature, the vesico-vesical refex are ambulatory surgical visits. A more complex voiding refex, The economic burden of pediatric urinary mediated at the level of the pons and midbrain, incontinence is diffcult to quantify. During currently available on aggregate direct costs for this transitional period, functional bladder capacity inpatient, outpatient, or surgical venues. Between 2 and 3 procedures has increased steadily during the past years of age, children attain the ability to volitionally decade. During this period, an Enuresis denotes a physiologically coordinated adult pattern of daytime urinary control emerges, void occurring at an inappropriate or socially characterized by a stable, quiescent bladder. The majority of urine into bed or clothes and two occurrences per children master toileting prior to entrance into school, week for at least three months, causing clinically (i. Beyond this age, signifcant distress or impairment in social, incontinence becomes an increasing social concern. The child must have reached an age at voiding control and found that 26% of children had which continence is expected (a chronological age of 5 attained daytime continence by the age of 24 months, years, or a mental age of 5 years for a developmentally 52. Bloom and colleagues studied 1,186 exclusively to the direct physiological effects of a normal children and found that the age at which substance or general medical condition (5). Toilet training Etiologic Classifcation of Pediatric Urinary occurred slightly earlier in females (3). Incontinence Defning pediatric urinary incontinence Childhood urinary incontinence can be classifed has historically been complicated by the lack of as organic or functional. Organic incontinence refers standardized defnitions for pediatric voiding to an underlying disease process, which can be either disorders. Structural incontinence includes reconstructed urethra and is stratifed as follows: diseases such as exstrophy-epispadias complex, stress incontinence, the involuntary loss of urine ectopic ureter, and posterior urethral valves. The prevalence of overfow incontinence, any involuntary loss of urine functional incontinence in the pediatric population associated with overdistension of the bladder; merits special focus. This symptom complex is the result of overactivity of 138 139 Urologic Diseases in America Urinary Incontinence in Children the detrusor muscle, which results in sudden bladder This leads to trapping of urine in the vagina. Dysfunctionalvoidingincludesseveralpatternsof Evaluation of a child with incontinence typically voiding with a single underlying feature: overactivity begins in an offce-based setting.