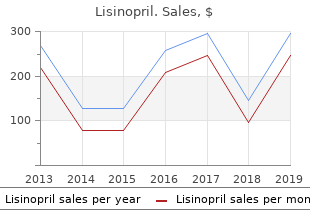
Lisinopril
Rochester College. E. Murak, MD: "Purchase online Lisinopril no RX - Safe Lisinopril".
The method can determine the effect of nanoparticle treatment on cell cycle progression as well as cell death discount lisinopril online american express arteria sa. In Vitro Target Organ Toxicity Toxicity screening for environmental exposure of nanoparticles has been reported (79) involving environmentally relevant exposure routes order lisinopril amex blood pressure for teens. However lisinopril 17.5mg on-line pulse pressure 42, in addition to in vitro examination of the so-called portal of entry tissues, a need for inclusion of target organs is also warranted. The liver and kidneys are generally selected as ideal candidates for these in vitro target organ toxicity studies since these organs are considered to be involved in accumulation, processing, and eventually clearance of nanoparticles. The liver is basically responsible for reticuloendothelial capture of nanopar- ticles, often due to phagocytosis of Kupfer cells for hepatic clearance of parenter- ally administered nanoparticles such as fullerenes, dendrimers, and quantum dots (80,81). In addition to accumulation, nanoparticles are shown to have detrimental effects on the liver function ex vivo and on hepatic morphology (82). Sprague-Dawley rat hepatic primary cells and human hepatoma HepG2 are generally used, since long time, for in vitro hepatic target organ toxicity assays due to their abundant availability and high metabolic activity (83). They are also chosen for toxicological studies, since hepatic primary cells in culture are more reflective of in vivo hepatocytes with regard to enzyme expression and specialized functions (84). Pharmacokinetic studies of parenterally administered carbon nanotubes in rodents have shown the urinary excretion as the principal mechanism of clear- ance (85–87). A variety of engineered nanoparticles, particularly doxorubicin- loaded cyanoacrylate nanoparticles, showed increased renal distribution and thus increased kidney toxicity (88–90). Kidney injury has been demonstrated in many other nanoparticles such nano-zinc particles in which severe histological alterations are observed in murine kidneys (91,92). These cell lines were used in variety of in vitro assays to evaluate cytotoxicity, mechanistic toxicology and pharmacology, etc. Oxidative Stress The generation of free radicals by nanomaterials of ambient or industrial origin is well documented (94,95). However, engineered nanomaterials such as fullerenes and polystyrene nanoparticles have also been shown to generate oxidative stress (56,96,97). At the end of exposure, dichlorofluorescein fluores- cence was determined at excitation wavelength of 485 nm and emission wavelength of 530 nm, respectively. Control cells cultured in Ag-free media (50 and 100 nm) were run in parallel to the treatment groups. Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Nanoparticle-induced cell death can occur by either necrosis or apoptosis, processes that can be distinguished both morphologically and biochemically. Apoptosis, 212 Murthy and Pathak morphologically, is characterized by perinuclear partitioning of condensed chromatin and budding of the cell membrane (105). The ability of nanoparticles, such as den- drimers and carbon nanotubes, to induce apoptosis has been demonstrated by in vitro studies (106,107). However, this link between oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and apoptosis has also been observed in man-made nanoparticles such as quantum dots and metals (76,109), water-soluble fullerenes derivatives (54,114), chitosan nanoparticles (115), and in various in vitro models. The loss of mem- brane potential causes the dye to dissipate from the matrix and can be measured in its monomeric state at emission wavelength 527 nm (green). Thus, the degree of mitochondrial membrane depolarization is measured as the proportion of green to red fluorescence. Pharmacological and Toxicological Characterization of Nanosystems 213 Mitochondrial membrane potential measurement can be an index of toxic- ity, which can be determined by the uptake study of rhodamine 123 according to the method of Wu et al. Cells were exposed to different concentrations of Ag (15 and 100 nm) for 24 hours. The fluorescence was determined at excitation wavelength 485 nm and emission wavelength 530 nm. Control cells cultured in Ag-free media (50 and 100 nm) were run in parallel to the treatment groups.
Diseases
- Blepharoptosis myopia ectopia lentis
- Enteropathica
- Gollop syndrome
- Anophthalmos, clinical
- Berylliosis
- Odontomicronychial dysplasia
- Chromosome 18, trisomy 18p
Monitoring of cyclosporin levels and possible adjustment of cyclosporin dosage should be considered when these drugs are co-administered buy lisinopril toronto blood pressure record chart uk. Musculoskeletal System: Exacerbation of gout during initial treatment purchase lisinopril 17.5 mg prehypertension education, arthralgias Haematological System: Eosinophilia and mild leukocytosis or leukopaenia Allopurinol! Store at room temperature 15-30°C; protect from light Compatible with: normal saline lisinopril 17.5mg for sale blood pressure drugs, D5W, D10W, Glucose and Sodium chloride, Hartmann’s. Do not mix with other medications – many medications with precipitate if mixed with aminophylline. Aminophylline should be ceased if the patient develops significant renal impairment. Theophylline directly relaxes the smooth muscle of the bronchial airway and pulmonary blood vessels, thus acting mainly as a bronchodilator and smooth muscle relaxant. It has also been demonstrated that aminophylline has a potent effect on diaphragmatic contractility in normal persons and may then be capable of reducing fatigability and therapy improve contractility in patients with chronic obstructive airway disease. Underlying seizure disorders (unless receiving appropriate anticonvulsant medications). Serious side effects such as ventricular arrhythmias, convulsions or even death may appear as the first sign of toxicity without any previous warning. A serum concentration measurement is the only reliable method of predicting potentially life-threatening toxicity. Theophylline products may cause or worsen arrhythmias and any significant change in rate and/or rhythm warrants measurement of a serum level and consideration of cessation of the drug. Nervous System: Headaches, reflex hyperexcitability, muscle twitching, clonic and tonic generalized convulsions. Administration via a central line is preferred Store at room temperature; do not refrigerate. Hypotension should be treated by vasopressor drugs, positive inotropic agents, and volume expansion. Additional measures including drug therapy and/or temporary pacing may be required if bradycardia does not resolve. Rare cases of fatal hepatocellular necrosis after treatment with amiodarone have been reported. Like all antiarrhythmic agents, amiodarone may cause a worsening of existing arrhythmias or precipitate a new arrhythmia. There have been reports of acute-onset (days to weeks) pulmonary injury in patients treated with amiodarone. Findings have included pulmonary infiltrates on X-ray, bronchospasm, wheezing, fever, dyspnea, cough, haemoptysis, and hypoxia. Laboratory Tests: Consider measurement of thyroid function as a baseline (if not measured previously). Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions Amiodarone alters the results of thyroid-function tests, causing an increase in serum T4 and serum reverse T3, and a decline in serum T3 levels. Antiarrhythmics: in general, any added antiarrhythmic drug should be initiated at a lower than usual dose with careful monitoring. This drug is not recommended for use during the acute recovery phase following myocardial infarction.
Order lisinopril cheap online. Harbor Freight Blood Pressure Monitor Review.
He is the Health Law and Ethics Editor of the Journal of the American Medical Association lisinopril 17.5mg without a prescription blood pressure medication beginning with r. In the wake of September 11 lisinopril 17.5 mg on line arrhythmia omega 3, 2001 purchase lisinopril 17.5 mg mastercard prehypertension spanish, the Center for Law and the Public’s Health drafted the Model Emergency Health Powers Act to combat bioterrorism and other emerging health threats. Professor Gostin was a member of the President’s Task Force on National Health Care Reform. His principal areas of work were on the ethical foundations of the new health care sys- tem, public health, and privacy. He was formerly executive director of the 331 Copyright © National Academy of Sciences. In the United Kingdom, Professor Gostin was the chief executive of the National Council for Civil Liberties, legal director of the National Association of Mental Health, and faculty member of Oxford University. Professor Gostin’s latest books are both published by the University of California Press and the Milbank Memorial Fund: Public Health Law: Power, Duty, Restraint (2000) and Public Health Law and Ethics: A Reader (2002). Freed Professor of Govern- ment and director of the Center for American Political Studies in the Faculty of Arts and Sciences at Harvard University. For the 2011-2012 academic year, he was a Walter Channing Cabot Faculty Fellow at Harvard and a visiting researcher at the Institut d’Études Politiques at the Université de Strasbourg in France. He graduated from Georgetown University in 1989 with distinction in government and received his doctorate in political science from the University of Chicago in 1996. He taught previously at Princeton University (1995-1998) and the University of Michigan (1998- 2002). Professor Car- penter mixes theoretical, historical, statistical, and mathematical analyses to examine the development of political institutions, particularly in the United States. He focuses upon public bureaucracies and government regulation, particularly regulation of health and fnancial products. Professor Carpenter has held fellowships from the John Simon Guggenheim Founda- tion, the Radcliffe Institute for Advanced Study, the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences, the Brookings Institute, and the Santa Fe Institute. He has received grants from the National Endowment for the Humanities, the National Science Foundation, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, the Alfred P. In addition to his ongoing teaching and scholarship on the political economy of government regula- tion and health, Professor Carpenter has recently launched a long-term project on petitioning in North American political development, examining comparisons and connections to petitioning histories in Europe and India. He hopes to draw upon the millions of petitions in local, state, and federal archives to create an educational, genealogical, and scholarly resource for citizens, students, and scholars. He qualifed as a medical doctor from Leiden Uni- versity in the Netherlands and received a Ph. He is director of essential medicines and pharmaceutical policies and chair of the Interagency Pharmaceutical Coordination Group. He has published more than 50 scientifc papers in peer-reviewed journals and teaches every year at international courses all over the world. In 1996 he was invited to become a fellow of the Royal College of Physicians in Edinburgh, Scotland, and in 1998, he received an honorary doctorate of science from the Robert Gordon University in Aberdeen, Scotland. She is also adjunct professor in medicine with the University of Washington School of Medicine. She has worked extensively in the areas of trade policy and disease control and telecommunications and disease surveillance and alert systems. Food and Drug Administraiton pharmaceutical control laboratory operations and more than 10 years of service as an elected expert on the Committee of Revision of the U. He is also a charter member and elected fellow of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists. He oversees the work of about 20 staff to provide technical assistance to developing countries to strengthen quality assurance and quality systems for pharmaceuticals. He worked in the pharmaceutical industry for Wyeth and Pfzer for a combined 12 years as senior principal scientist.
Boxberry (Wintergreen). Lisinopril.
- Headache, minor aches and pains, stomachache, gas (flatulence), fever, kidney problems, asthma, nerve pain, gout, arthritis, menstrual period pains, arthritis-like pain (rheumatism), and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Wintergreen.
- What is Wintergreen?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Wintergreen work?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96762