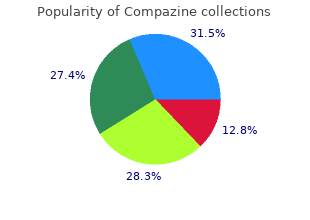
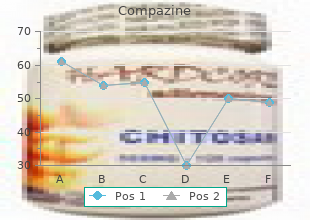
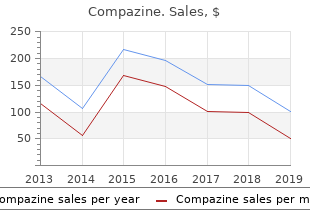
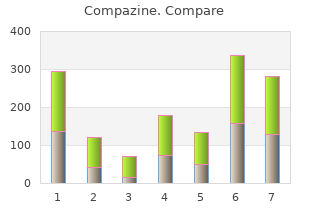
Compazine
Whitman College. E. Kippler, MD: "Purchase Compazine online - Quality Compazine no RX".
Since example of the immunosuppressants aza- β1-blockers have a relatively large margin of thioprine and mercaptopurine buy 5 mg compazine with amex symptoms your period is coming. A genetic exami- of the diminished purine methylation discount compazine 5 mg on-line medications you cant crush, the nation before the start of drug therapy will plasma level of active drug rises and buy compazine 5mg otc treatment pink eye, hence, be a sensible precaution, particularly when the risk of toxic bone marrow damage rises. Other genetic variants of drug metabolism may have a similar impact: a defect of N- acetyltransferase 2 impedes the N-acetyla- tion of diverse drugs, including isoniazid, hydralazine, sulfonamides, clonazapam, and nitrazepam. Genetic variants of pharmacodynamics Drug in plasma β1-Receptor antagonist Time β1-Receptor gene Time Arg389 Gly389 Desired hypotensive Hypotensive effect Hypotensive effect effect too small Luellmann, Color Atlas of Pharmacology © 2005 Thieme 80 Drug-independent Effects trial, neither the patients nor the treating Placebo (A) physicians know which patient is given drug A placebo is a dosage form devoid of an and which placebo. Ad- drug to placebo and vice versa can be made ministration of a placebo may elicit the de- in a successive phase of treatment, the cross- sired effect (relief of symptoms) or unde- over trial. Physicians may consciously or uncon- sciously communicate to the patient Homeopathy (B) is an alternative method of whether or not they are concerned about therapy, developed in the 1800s by Samuel the patient’s problem, or are certain about Hahnemann. His idea was this: when given the diagnosis and about the value of pre- in normal (allopathic) dosage, a drug (in the scribed therapeutic measures. In the care of senseofm edicam ent)willproduceacon- a physician who projects personal warmth, stellation of symptoms; however, in a pa- competence, and confidence, the patient in tient whose disease symptoms resemble just turnfeelscomfortandlessanxietyandopti- this mosaic of symptoms, the same drug mistically anticipates recovery. The physical (simile principle) would effect a cure when condition determines the psychic disposi- given in a very low dosage (“potentiation”). Consider gravely The body’s self-healing powers were to be wounded combatants in war, oblivious to properly activated only by minimal doses of their injuries while fighting to survive, only the medicinal substance. The homeopath’s to experience severe pain in the safety of the task is not to diagnose the causes of morbid- field hospital; or the patient with a peptic ity, but to find the drug with a “symptom ulcer caused by emotional stress. With the be impossible to decide whether therapeutic accompaniment of a prescribed (“ritual- success is attributable to the drug or to the ized”) shaking procedure, the drug is then therapeutic situation. For serious suggestive powers of the homeopath and the diseases, the comparison group has to be expectancy of the patient. When an illness is treated with the best therapy known to date, strongly influenced by emotional (psychic) rather than a placebo. To be acceptable, the factors and cannot be treated well by allo- test group receiving the new medicine must pathic means, a case can be made in favor of showa result superior to that of the compar- exploiting suggestion as a therapeutic tool. A retrospective (case–control) study follows patients backward in time, the decision to analyze being made only after completion of therapy. Therapeutic effects resulting from physican’s power of suggestion Conscious Conscious and and unconscious unconscious signals: expectations Mind language, facial expression, gestures Well- being complaints Placebo Effect: – wanted – unwanted Body Physician Patient B. Homeopathy: concepts and procedure “Similia similibus curentur” Homeopath Patient “Drug” Normal, allopathic dose symptom profile Dilution “effect reversal” Very low homeopathic dose elimination of disease symptoms corresponding to allopathic symptom “profile” “Potentiation” increase in efficacy Profile of disease symptoms with progressive dilution Symptom “profile” “Drug diagnosis” Homeopathic remedy (“simile”) Stock solution Dilution 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 D9 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 11000000000 Luellmann, Color Atlas of Pharmacology © 2005 Thieme Luellmann, Color Atlas of Pharmacology © 2005 Thieme Systems Pharmacology Drugs Acting on the Sympathetic Nervous System 84 Drugs Acting on the Parasympathetic Nervous System 102 Nicotine 112 Biogenic Amines 116 Vasodilators 122 Inhibitors of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System 128 Drugs Acting on Smooth Muscle 130 Cardiac Drugs 132 Antianemics 140 Antithrombotics 144 Plasma Volume Expanders 156 Drugs Used in Hyperlipoproteinemias 158 Diuretics 162 Drugs for the Treatment of Peptic Ulcers 170 Laxatives 174 Antidiarrheals 180 Drugs Acting on the Motor System 182 Drugs for the Suppression of Pain 194 Antipyretic Analgesics 196 Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs 200 Local Anesthetics 202 Opioids 208 General Anesthetics 214 Psychopharmacologicals 220 Hormones 238 Antibacterial Drugs 268 Antifungal Drugs 284 Antiviral Drugs 286 Antiparasitic Drugs 292 Anticancer Drugs 298 Immune Modulators 304 Antidotes 308 Luellmann, Color Atlas of Pharmacology © 2005 Thieme 84 Drugs Acting on the Sympathetic Nervous System tion). In simplistic terms, activation of the Sympathetic Nervous System sympathetic division can be considered a Inthecourseofphylogenyanef cientcon- m eansbywhichthebodyachievesastate trol system evolved that enabled the func- of maximal work capacity as required in tions of individual organs to be orchestrated fight-or-flight situations. The splanchnic blood vessels diverts blood into somatic nervous system, comprising exte- vascular beds in muscle. It adjusts inter- theliverandfreefattyacidsfrom adipose nal organ functions to the changing needs of tissue must be released into the blood. Neural control permits very bronchi are dilated, enabling tidal volume quick adaptation, whereas the endocrine and alveolar oxygen uptake to be increased. Both are made up work capacity, albeit without energy-con- of centrifugal (efferent) and centripetal (af- suming muscle activity. In manyorgansinnervated by both branches, respective activation of the sympathetic and parasympathetic input evokes opposing responses.
The concentration of the drug In the laboratory the strain of pathogen purchase compazine 5mg amex symptoms and diagnosis, the number of in a patient’s body as a function of time is determined infecting organisms compazine 5 mg medicine bg, the culture medium cheap 5 mg compazine free shipping medicine you cannot take with grapefruit, the antibiotic by the dose administered and the drug’s pharmacoki- concentration, and the duration of antibiotic exposure netics in that patient. Aluminum, calcium, man disease is complex, as it depends on a complex and magnesium ions in antacids or dairy products form patient–drug–pathogen interaction. This interaction has insoluble chelates with all tetracyclines and inhibit their six components: absorption. Food inhibits tetracycline absorption but • Pharmacokinetics: What the patient does to the enhances doxycycline absorption; food delays but does drug. For example, a patient with renal failure not diminish metronidazole absorption; fatty food en- will have diminished renal clearance of gen- hances griseofulvin absorption. The chemical structure of a drug determines which • Pharmacodynamics: What the drug does to the enzymes metabolize it; a drug that fails to cross the cell patient. For example, erythromycin stimulates membrane because of its polarity or size will be unme- gut motilin receptors and may induce nausea. Systemic use of drugs • Immunity: What the patient does to the that are poorly absorbed or are destroyed by the gas- pathogen. Of course, if the goal is to attack pathogens in disease in spite of receiving a course of postex- the gastrointestinal tract, then poor gastrointestinal ab- posure prophylactic antituberculosis chemo- sorption may be an advantage. For cludes both nonspecific complement-mediated example, imipenem is hydrolyzed by renal dipeptidase opsonization and specific antibody- and cell- to a metabolite that is inactive against bacteria but is mediated immunity. The intrahepatocellular concentration of chloroquine is • Resistance: What the pathogen does to the drug. For example, some strains of Pseudomonas Macrolides and fluoroquinolones are also selectively aeruginosa produce a plasmid-mediated adeny- partitioned into cells, which accounts in part for their ef- lase that inactivates gentamicin by chemically ficacy against mycoplasma and chlamydia, both intra- altering its structure. For example, acyclovir triphosphate, free level and decreases the compound’s glomerular fil- the phosphorylated derivative of acyclovir, tration. As mentioned earlier, pharmacokinetics is not solely the property of a drug but instead is the consequence of interactions between the drug and the physiology of the Pharmacokinetics patient. Thus, statements like “the half-life of gentam- To be clinically useful, a chemotherapeutic drug must icin is 2 hours” are not very useful, as the half-life is have both selective toxicity against pathogens and fa- likely be longer or shorter in a given individual patient. The concentrations of chemotherapeutic drugs in Toxicity is most likely in tissues that interact with blood plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, or ascites fluid the drug. For example, gentamicin is polycationic and can be measured to determine whether sufficient drug is binds to anionic phospholipids in the cell membranes of present to inhibit or kill a given pathogen and to ensure renal proximal tubular cells, where it inhibits phospho- that the concentration is not so high as to be toxic to the lipases and damages intracellular organelles. Some adverse reactions are unrelated to either al- In severe bacterial infections that are difficult to erad- lergy or overdose; these are termed idiosyncratic. For icate, such as endocarditis or osteomyelitis, it may be im- instance, sulfonamides may precipitate acute hemolysis portant to ensure that the patient’s serum remains bacte- in some people having a glucose-6-phosphate dehydro- ricidal at the lowest, or trough, concentration in the genase deficiency. Dilutions of patient’s serum can be incu- Many antibiotics alter the enteric microbial flora, bated with the organism isolated from the patient and the particularly if high concentrations reach the colon. Treatment is considered adequate if the thereby removing their inhibitory effects on potentially serum remains bactericidal at a dilution of 1:8. In the case of antibiotic chemotherapy, the ideal phar- difficile, which then elaborates its toxin in high concen- macodynamic response is usually no pharmacodynamic tration. This toxin can cause pseudomembranous colitis, response; the pharmacological target is not normal hu- which can be fatal if not recognized and treated. The less selective the chemother- adequate immune function; however, some antibiotics apeutic drug, the greater the severity of adverse effects.
Opioids Pethidine is eight to ten times less potent than morphine cheap 5 mg compazine with mastercard medications and side effects, with a short half-life (morphine and diamorphine) should has poor and variable oral absorption purchase compazine with a visa 2c19 medications, with a short dura- be used as first-line agents for acute pain but may be tion of action in the range of 2–3 h purchase compazine 5mg fast delivery medicine 4h2. Cross-tolerance between drugs is in- complete, so when one drug is substituted for another, the Tramadol equi-analgesic dose should be reduced by 50%. The only exception is methadone, which should be reduced by Tramadol is presented as a mixture of two stereoisomers. Opioid rotation is commonly used in cancer-related is a centrally acting analgesic with relatively weak m-opioid and chronic non-malignant pain as a means of reducing receptor activity. Naloxone is a competitive antagonist at m-, d-, k-, and **Potency relative to morphine: for example, hydromorphone is six s-opioid receptors and acts to reverse the effects of most opi- times more potent than an equal dose of morphine when given oid analgesics. Patients on long-term opioid therapy should not be given mixed agonist/antagonist drugs, as they Codeine 60 mg 5 mg can precipitate withdrawal. Dihydrocodeine 60 mg 8 mg Tramadol 50 mg 10 mg Addiction is a behavioural problem characterised by drug- seeking activity in the individual in order to experience its Meptazinol 200 mg 8 mg psychotropic effects. This drug-seeking behaviour may per- sist despite the knowledge that continued use of the drug Buprenorphine 200 10 mg will result in considerable physical, emotional, social or eco- sublingual micrograms nomic harm. The risk of iatrogenic addiction in patients pre- scribed opioids for cancer-related pain is believed to be extremely low. Physicians, particularly in hospitals, are often guilty of withholding or under- Although the use of strong opioid analgesics in cancer- prescribing opioids for drug-addicted patients in acute related pain is well established, physicians are often reluc- pain. This stems from unfounded fears of ‘worsening’ the tant to prescribe opioids in acute, and especially in chronic, addiction, distrust of the patient’s motives or misguided at- non-malignant pain. The reasons for this reluctance may stem should attempt to establish the patient’s daily opioid intake from previous experiences of the genuine problems associ- prior to hospital admission. The patient should then be ated with long-term opioid use in patients or, more often, maintained with an equivalent daily dose of opioid medi- due to the perception of opioids as dangerous and addictive cation throughout their admission. Patients and physicians also frequently confuse aware that the strength of street drugs is highly variable. The addicted patient may also have an acute medical con- dition that alters opioid pharmacokinetics unpredictably. It Tolerance indicates the need to increase the dose of a drug is safer, therefore, to first prescribe an appropriate dose of with time to achieve the same analgesic effect. It is due to an opioid with a short duration of action on an ‘as required’ physiological adaptation to the drug. In practice, tolerance basis, in order to assess opioid requirements, before con- can be managed by increasing the dose of the opioid drug version to longer-acting opioids for maintenance. The opioid-addicted patient with acute pain will require constipation)isoftenless predictable,andthedevelopment appropriate analgesia in addition to the calculated mainte- of side-effects may prevent further escalation of the drug. Non-opioid analgesics are useful adjuncts, but It is important to distinguish a gradual reduction in should not be used as a substitute for opioid analgesia. The efficacy of an analgesic that is due to the development of use of opioid agonist–antagonist compounds in known or tolerance from the onset of pain due to progression of suspected active opioid addicts is absolutely contraindi- the underlying disease process or new pathology. Dependence is the physical manifestation of tolerance and its effects are observed soon after abrupt withdrawal of a long-term opioid. The severity of withdrawal symp- toms varies depending on the patient, the drug and the length of treatment, and includes symptoms such as 4Opioids for persistent pain. These agents provide an ‘opioid-sparing’ effect and for the tertiary amine tricyclic drugs, such as amitri- are effective for the treatment of neuropathic pain associ- ptyline, doxepin and imipramine. In chronic non-malignant pain, tricyclic antidepressants (such as desipramine and no- co-analgesics are frequently used as ‘first-line’ drugs, and rtriptyline) have fewer side-effects and are preferred form the mainstay of treatment for chronic neuropathic when there are serious concerns about sedation, anticho- pain. There is little evidence, however, to suggest that duloxetine is more efficacious compared Multipurpose adjuvant analgesics to tricyclic antidepressant drugs for the treatment of neuropathic pain.
The bond is to hinder intercalation of any apolar (un- reversible and is typical of most drug–recep- charged) molecules buy 5mg compazine mastercard treatment 4 ulcer. Since a drug usually at- other buy compazine with american express treatment zygomycetes, H2O molecules squeeze apolar par- taches to its site of action by multiple con- ticles from their midst discount 5 mg compazine with amex medicine 6 times a day. Accordingly, in the tacts, several of the types of bonds described organism, apolar particles such as fatty acid below may participate. Attraction between ions of opposite charge is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them; it is theinitialforce drawingachargeddrug toits binding site. Dipole–ion interaction: When bonding electrons are asymmetrically distributed over the atomic nuclei involved, one atom will bear a negative (δ–), and its partner a positive (δ+) partial charge. Hydrophobic interaction δ+ H H “Repulsion” of apolar δ−O apolar particle in polar solvent ( H2O) polar Apolar acyl chain Insertion in apolar membrane interior Adsorption to apolar surface Luellmann, Color Atlas of Pharmacology © 2005 Thieme 60 Drug–Receptor Interaction nist attaches to the inactive receptor without Agonists—Antagonists altering its conformation. An agonist (A) has af nity (tendency to ad- here) for a receptor and affects the receptor Agonist stabilizes spontaneously occurring proteininsucham annerastocausea active conformation. Usually, however, the statistical change in cell function) depends on the ef- probabilityofsuchaneventissosm allthat fectiveness of signal transduction steps a spontaneous excitation of the cells remains (p. Selective binding of the ago- The maximal effect of an agonist may al- nist can occur only to the active conforma- readyoccur whenonlya fraction of the avail- tion and thus favors the existence of this able receptors is occupied (B,agonistA). The antagonist shows af nity only for Another agonist (agonist B), possessing theinactivestate, promoting existenceof the equal af nity but less ability to activate the latter. If the system has little spontaneous receptor and the associated signal transduc- activity, no measurable effect will result tion steps. However, if the produce a smaller maximal effect even if all system displays high spontaneous activity, receptors are occupied—smaller ef cacy. Thepotency opposite to that of an agonist: inverse ago- of an agonist is characterized by the concen- nist. According petitive antagonists possess af nity for the to this model, a partial agonist haslessse- receptors, but their binding does not elicit a lectivity for the active state; however, to a change in cell function. The agonist binds to the inactive receptor and thereby causes the resting conformation to change into the active state. Molecular mechanisms of drug–receptor interaction Agonist Antagonist Antagonist Agonist Rare spontaneous transition Receptor inactive active Agonist Antagonist Antagonist Agonist induces active occupies selects inactive selects active conformation of receptor receptor receptor receptor protein without effects conformation conformation B. Competitive antagonism Agonist effect 0 1 10 100 1000 10000 Concentration of antagonist Agonist concentration (log) Luellmann, Color Atlas of Pharmacology © 2005 Thieme 62 Drug–Receptor Interaction of the enantiomers will have optimal fit. A racemate consists of amolecule propranolol has an af nity 100 times that of and its corresponding mirror image which, the (R)-(+) form. For instance, (–)-dobutamine is an agonist at Nonchiral stereoisomers are called diaste- β-adrenoceptors, whereas the (+)-enantio- reomers (e. As a result of enzymatic activity, how- amine, the (+)-enantiomer has af nity at β- ever, only one of the enantiomers is usually adrenoceptors that is 10 times higher than found in nature. However, the α-adrenoceptor of oscillation of linearly polarized light in stimulant action is due to the (–)-form (see oppositedirections;hencetheyarereferred above). The direction of rotation in drug interactions with enzymes and gives no clue concerning the spatial struc- transport proteins. The absolute configura- play different af nities and reaction veloc- tion, as determined by certain rules, is ities. The enantiomers of a racemate and L-forms is possible by reference to the can differ suf ciently in their pharmacody- structure of D-andL-glyceraldehyde. If a receptor has sites for three of the substituents (sym- bolized in B by a cone, sphere, and cube) on the asymmetric carbon to attach to, only one Luellmann, Color Atlas of Pharmacology © 2005 Thieme Enantioselectivity of Drug Action 63 A. Glutamate and to bind mediator substances and transduce glycine both act via ligand-gated ion chan- this binding into an effect, i.